Do you remember that sinking feeling of dread in accounting class when you stumbled upon problem 27 in the 1-M Mastery textbook? It seemed to defy logic, its numbers twisting into an intricate maze that promised headaches and a plummeting grade. Fear not, aspiring accountants! This article is your guide to conquering problem 27, demystifying its complexities and helping you unlock the secrets to achieving mastery in accounting.
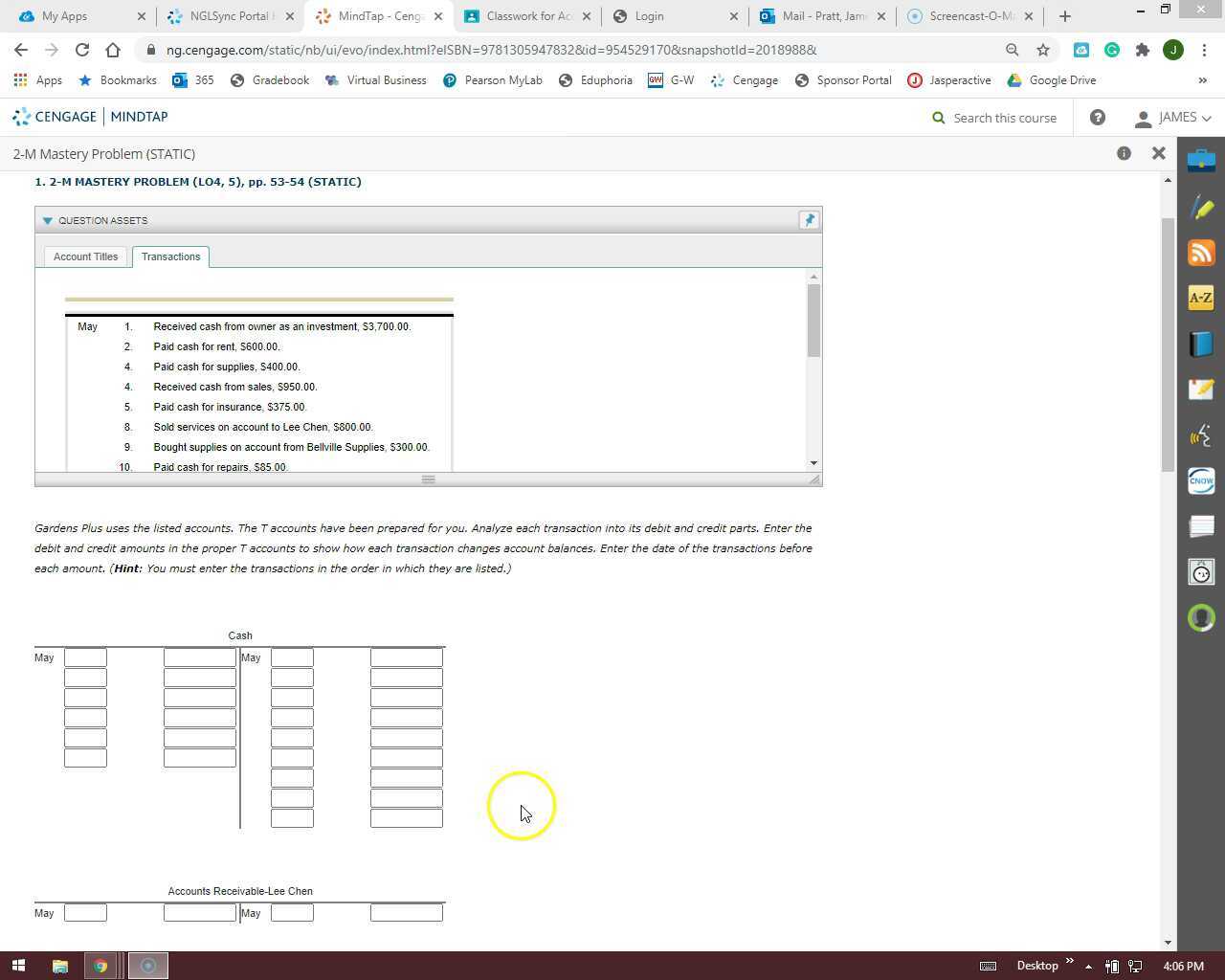
Image: screencast-o-matic.com
1-M Mastery is a foundational textbook for budding accountants, challenging students to develop a solid understanding of financial accounting principles and apply them to real-world scenarios. Problem 27, often the bane of many students’ existence, focuses on a specific area of accounting that demands a deep grasp of principles and a keen eye for detail. It’s a hurdle, yes, but a hurdle that, once overcome, can propel you toward a greater understanding of the subject.
Understanding the Challenge: Decoding the Components of Problem 27
Problem 27 typically presents a complex financial scenario, often involving multiple transactions and diverse accounting principles. Let’s break down the key elements that make this problem so challenging:
1. Multiple Transactions:
Problem 27 often presents a series of transactions involving various financial instruments, like accounts receivable, inventory, liabilities, and more. Each transaction impacts different accounts, requiring careful analysis to determine the correct entries and their corresponding impact on the financial statements.
2. Complex Accounting Principles:
The problem might involve a mix of accounting standards, such as generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). Each standard has unique rules for handling transactions and preparing financial statements.
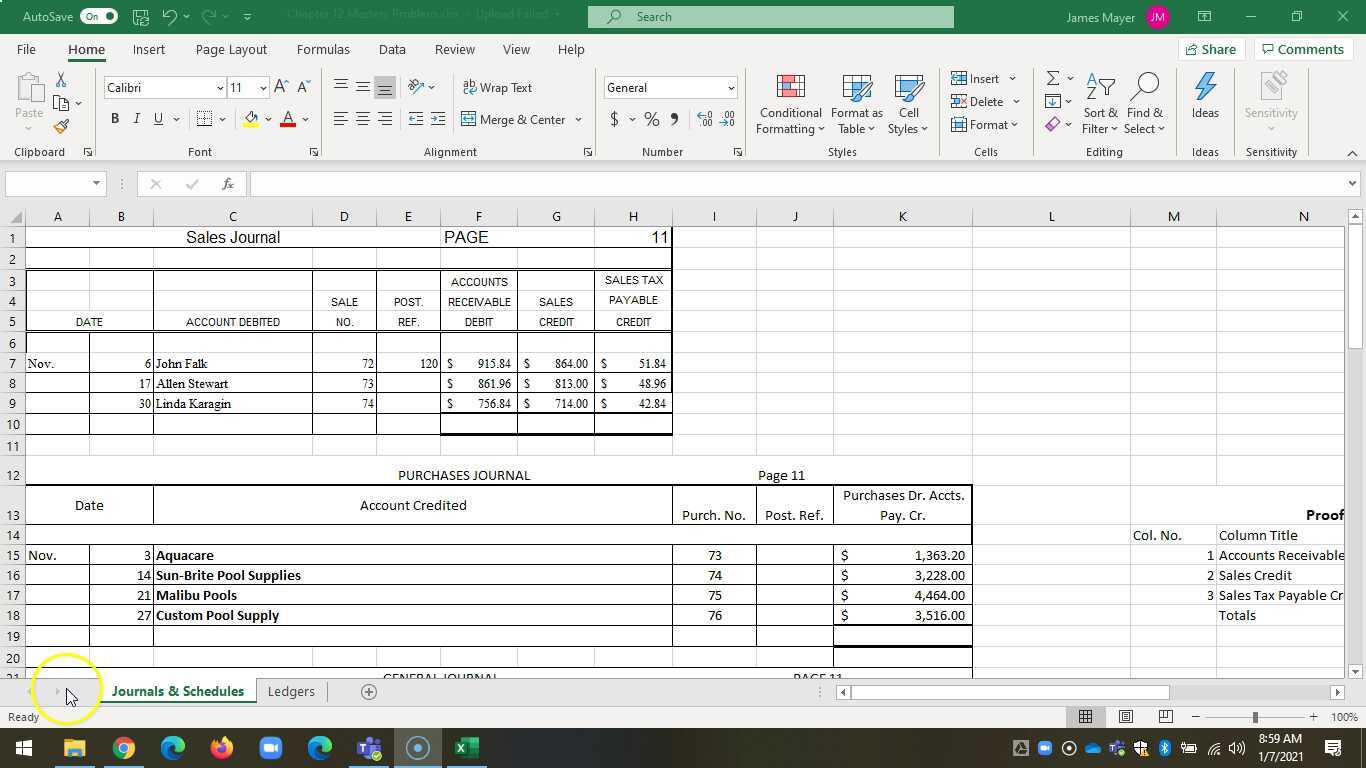
Image: screenpal.com
3. Diverse Accounting Methods:
Problem 27 can incorporate different accounting methods like the accrual method or the cash method. Understanding the difference between these methods and their impact on financial reporting is crucial for solving the problem accurately.
4. Financial Statement Analysis:
The problem might require a thorough analysis of financial statements, including the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement. This involves identifying and interpreting key financial ratios, trends, and relationships within the data.
Navigating the Maze: A Step-by-Step Approach
Tackling problem 27 is a journey of meticulous analysis and strategic application of accounting principles. Here’s a step-by-step approach to help you achieve mastery:
Step 1: Read and Understand the Problem Statement
Read the problem carefully and thoroughly. Identify the specific transactions involved, the accounting principles mentioned, and the financial statements required.
Step 2: Analyze Each Transaction
Break down each transaction into its individual components. Determine the accounts involved, their debit or credit nature, and the corresponding amount. Utilize the accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Equity) as your guiding framework.
Step 3: Apply the Correct Accounting Principles
For each transaction, apply the relevant accounting principles and standards outlined in the problem or in your textbook. This might involve accrual accounting, matching principles, or specific accounting standards governing inventory, depreciation, or revenue recognition.
Step 4: Record Journal Entries
Based on your analysis, prepare the journal entries for each transaction. This involves recording the debit and credit accounts with the correct amounts.
Step 5: Prepare Trial Balances and Financial Statements
After recording all journal entries, prepare a trial balance to ensure the debit and credit balances are equal. Then, use this information to construct the various financial statements including the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement.
Step 6: Review and Analyze
Carefully review your work. Look for any errors in applying principles, recording transactions, or preparing financial statements. Analyze the results of your calculations and compare them with the expected outcome.
Mastering the Basics: Essential Accounting Concepts for Problem 27
Understanding the basics lays the foundation for conquering problem 27. Here are some key accounting concepts to master:
1. The Accounting Equation
The accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Equity) is the bedrock of accounting, representing the fundamental relationship between assets, liabilities, and equity. It highlights the fact that organizations must use their financial resources to finance their business operations. This equation serves as a constant check in solving problems and ensuring the accounting equation is always in balance.
2. Debit and Credit Accounting
The debit/credit system underpins double-entry bookkeeping. It ensures every transaction is recorded twice, with equal debits and credits. Understanding which accounts are debited and which are credited is crucial for accurate accounting.
3. Accrual Accounting
Most accounting problems, including problem 27, utilize the accrual accounting method. This method recognizes revenues when earned and expenses when incurred, regardless of whether cash is received or paid.
4. Common Financial Ratios
Understanding key financial ratios helps you analyze a company’s performance and financial health. These include liquidity ratios, profitability ratios, leverage ratios, and efficiency ratios.
Beyond the Textbook: Practical Applications and Real-World Connections
While problem 27 may seem theoretical, its principles have real-world implications. Accounting professionals use these same principles daily to:
- Track financial performance of companies
- Make informed business decisions
- Manage financial risks
- Prepare financial reports for investors and stakeholders
By gaining mastery over problem 27, you develop the skills necessary to understand and analyze complex financial information, a skill invaluable in any accounting-related career.
Overcoming the Fear of Accounting: Tips for Success
Here are some additional tips to help you conquer the challenge of accounting problems like problem 27:
- Seek Help: Don’t hesitate to ask your professor, teaching assistant, or classmates for help.
- Practice Regularly: The best way to master accounting is through constant practice. Work through similar problems and examples.
- Understand the Fundamentals: Ensure you have a solid grasp of the basic accounting principles before tackling complex problems.
- Visualize the Information: Use diagrams, tables, and charts to visualize the accounting relationships and financial information.
- Embrace Technology: Utilize accounting software or online tools to help with calculations and analyses.
1-M Mastery Problem Accounting Answers Pg 27
Conclusion: The Path to Accounting Mastery
Conquering problem 27 is a testament to your commitment to becoming a skilled accountant. It demonstrates your ability to analyze complex scenarios, apply relevant accounting principles, and interpret financial information. Remember, this problem is not an insurmountable obstacle but an opportunity to enhance your understanding of accounting and develop valuable skills that can open doors to a rewarding career in the world of finance. So, embrace the challenge, take your time, practice diligently, and unlock the secrets to achieving mastery in accounting. The journey may be challenging, but the rewards are well worth the effort.





