Remember those high school chemistry classes, filled with cryptic symbols and seemingly endless rules? I certainly do. One of the most daunting tasks back then was naming chemical compounds. The sheer number of elements, the varying charges, and the bizarre prefixes – it all felt like an intricate puzzle with no clear solution. However, amidst this chemical chaos, a friendly rivalry emerged – the battle between ionic and covalent compound naming.

Image: fotokolekcija.blogspot.com
Each type of compound, with its unique characteristics and bonding patterns, presented its own set of rules. Naming ionic compounds, with their predictable cation-anion interactions, felt like a straightforward race. But covalent compounds, with their shared electrons and variable prefixes, seemed to throw a curveball, making the race feel more like a confusing obstacle course.
The Ionic Naming Game: Predictability and Consistency
Imagine a game where you have a set of building blocks, each with a specific color and shape. Ionic compounds are like those building blocks, with predictable charges and consistent naming patterns.
The basic premise of ionic compound naming lies in identifying the cation (positively charged ion) and the anion (negatively charged ion). The cation, usually a metal, retains its name. The anion, often a nonmetal, is named according to a set of rules.
Ionic Naming Rules:
- The cation (metal) name remains the same. For example, Na+ is called sodium.
- The anion (nonmetal) name is modified by adding “-ide.” For example, Cl– is called chloride.
- Use Roman numeral to represent the charge on a metal cation, if it has multiple charges, For example, Fe2+ is called Iron(II)
These rules create a predictable framework for naming ionic compounds. For example, NaCl becomes sodium chloride, and MgBr2 becomes magnesium bromide. It’s like a clear path, where every step leads you closer to the finish line.
Covalent Naming Challenge: A Maze of Prefixes
Now, imagine venturing into a maze, where each path is labeled with a cryptic sequence of prefixes and suffixes. Covalent compounds, with their shared electron pairs and varied combinations, present such a challenge.
The complexity arises from the fact that nonmetals can form multiple bonds. The number of atoms of each element in a covalent compound is indicated by prefixes.
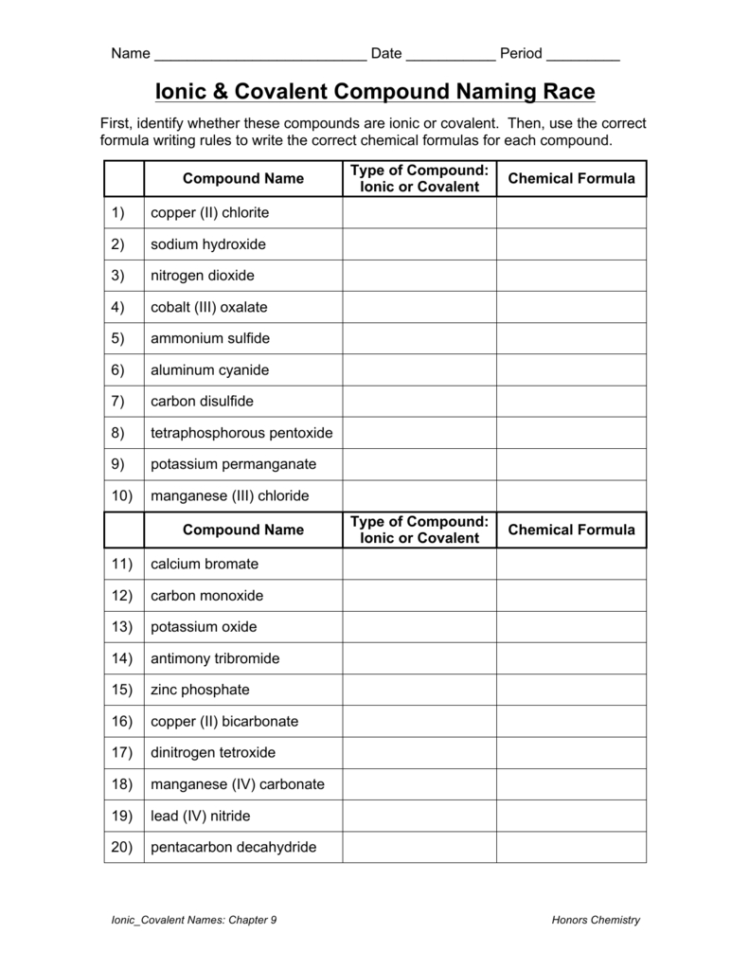
Image: db-excel.com
Covalent Naming Rules:
- The prefixes mono- (1), di- (2), tri- (3), tetra- (4), penta- (5), hexa- (6), hepta- (7), octa- (8), nona- (9), and deca- (10), are used to indicate the number of atoms of each element in the compound.
- The name of the element with the lower electronegativity usually comes first.
- The name of the second element usually ends in “-ide.”
- The prefix “mono-” is often omitted for the first element. For example, CO is called carbon monoxide, not monocarbon monoxide.
For example, CO2 becomes carbon dioxide, and N2O4 becomes dinitrogen tetroxide. Navigating this maze of prefixes requires careful attention and a keen eye for detail. It’s like solving a puzzle, where each piece must fit perfectly into the bigger picture.
The Naming Race: A Close Call
So, the race between ionic and covalent compound naming is truly a close one. Ionic compounds, with their straightforward naming rules, might seem like the early frontrunner. However, covalent compounds, despite their complexity, offer a unique challenge that appeals to those who thrive on intricate puzzles. In the end, it comes down to individual preference and the level of detail required for each type of compound.
Expert Tips for Mastering Chemical Nomenclature
As an experienced chemistry enthusiast, I’ve learned a few tricks along the way to navigate the world of chemical nomenclature. Here are some tips to help you ace the naming game:
- Practice, Practice, Practice. The key to mastering any chemical concept is practice. Write down the names of compounds, work through examples, and test yourself regularly. The more you do, the more confident you’ll become.
- Create flashcards. Flashcards are a great way to memorize the names of elements, prefixes, and suffixes. Carry them with you, and use them during your free time.
- Use online resources. There are many online resources available that can help you with chemical nomenclature. These resources often include interactive exercises, quizzes, and detailed explanations.
- Group study. Studying with friends can make the learning process more enjoyable and effective. Discuss difficult concepts, and help each other understand the material.
Remember, mastering the naming game is all about understanding the fundamental principles behind it. Once you grasp the core concepts, you’ll be able to navigate the world of chemical nomenclature with confidence and ease.
FAQs:
Q: What is the difference between ionic and covalent compounds?
A: Ionic compounds are formed by the electrostatic attraction between positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged ions (anions). Covalent compounds are formed by the sharing of electrons between atoms.
Q: Why are prefixes used in naming covalent compounds?
A: Prefixes are used in naming covalent compounds to indicate the number of atoms of each element present in the compound. This is because nonmetals can form multiple bonds, resulting in varying combinations.
Q: Is it necessary to memorize all the prefixes for covalent compound naming?
A: While memorizing the prefixes is helpful, it’s more important to understand the system of prefixes and how they are used. With practice, you’ll be able to apply the prefixes even if you don’t have them memorized.
Ionic And Covalent Compound Naming Race
Conclusion
So, who wins the ionic vs. covalent compound naming race? It’s a close call, but ultimately, it depends on your individual preference and the level of detail required. Both types of compounds present unique challenges and rewards, encouraging us to delve deeper into the fascinating world of chemistry.
Are you ready to take on the challenge and master the art of naming chemical compounds? Let us know in the comments below!





