Have you ever stared at a complex inheritance pedigree chart, feeling like you’ve stumbled into a tangled family tree with branches reaching back to the dawn of time? The world of genetics can be fascinating, but navigating the intricacies of intricate inheritance patterns can feel like deciphering a foreign language. This article will equip you with the keys to unlocking those genetic puzzles, guiding you through the labyrinth of complex inheritance practice problems and providing a comprehensive answer key to guide your understanding.
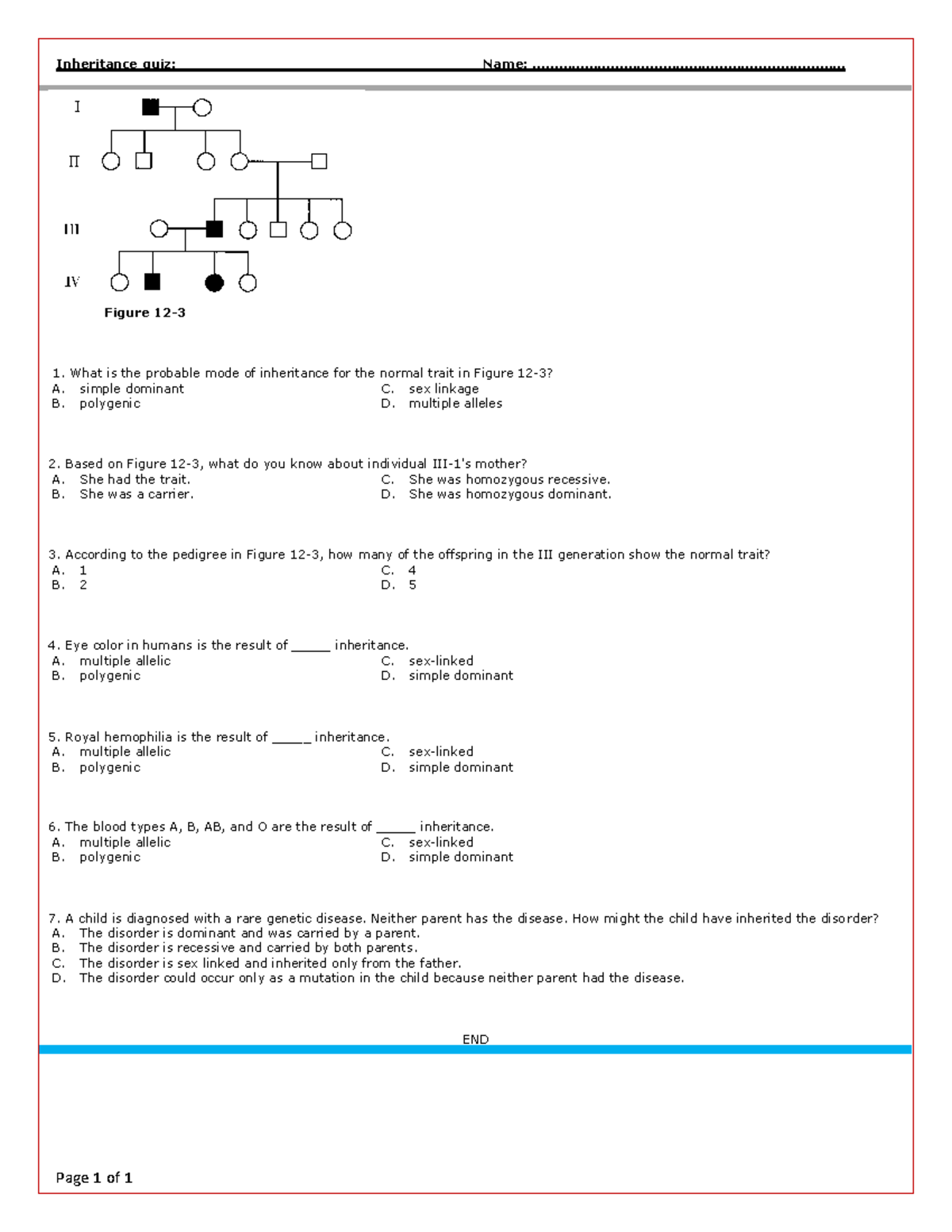
Image: www.studocu.com
Mastering the art of solving complex inheritance problems is crucial for anyone seeking a deeper understanding of genetics. Whether you’re a student delving into the world of biology, a budding geneticist, or simply a curious individual fascinated by the intricate mechanisms that govern life, this exploration will illuminate the path towards a clearer grasp of the fascinating world of inheritance.
Unveiling the Complexity: Beyond the Basics
Before we dive into the intricate patterns of complex inheritance, let’s establish a foundation. Remember those classic Mendelian genetics problems involving dominant and recessive alleles, neatly packaged into single-gene traits? Simple, right? But real-life inheritance often defies such neat categorization. That’s where complex inheritance comes into play. In this realm, multiple genes, environmental factors, and even chance contribute to the expression of a trait.
1. Polygenic Inheritance: The Cooperative Game of Genes
Imagine a trait like human height. It’s not simply determined by a single gene; instead, multiple genes work in concert, each contributing a small but significant piece to the overall picture. This cooperative phenomenon is known as polygenic inheritance. Each gene involved in a polygenic trait may have multiple alleles, adding layers of complexity to the inheritance pattern. The result? A continuous spectrum of possibilities rather than a clear-cut distinction between dominant and recessive phenotypes.
**Example:** Skin color is a classic example of polygenic inheritance. The more genes contributing towards melanin production, the darker the skin tone. This creates a wide range of skin hues, making it difficult to categorize individuals based on simple dominant/recessive relationships.
2. Epistasis: The Gene That Calls the Shots
But wait, there’s more! Sometimes, genes don’t just contribute equally; one gene can exert dominance over another, inhibiting its expression. This is known as epistasis. It’s like a kingpin gene setting the stage for other genes to play their part. The epistatic gene can mask the effects of other genes, regardless of their specific alleles.
**Example:** In labrador retrievers, coat color is influenced by two genes. One gene determines the pigment (black or brown), while the other determines the distribution of pigment (solid, black, or yellow). The “pigment distribution” gene exhibits epistasis over the “pigment” gene. If a dog has the recessive alleles for both genes, it will have a yellow coat, even if it carries the alleles for black pigment. The recessive alleles for the “pigment distribution” gene effectively mask the expression of the “pigment” gene.

Image: www.teacherspayteachers.com
Tackling the Challenge: Complex Inheritance Practice Problems
Now that we’ve delved into the complexities of inheritance patterns, it’s time to tackle some practice problems. This is where the fun (and sometimes frustration!) really begins. The key is to break down each problem systematically, considering all the relevant factors and the possible outcomes.
1. The Pedigree Puzzle: Tracing Patterns Through Generations
One common type of practice problem involves analyzing a pedigree chart, which is a family tree that maps out the inheritance of a specific trait through multiple generations. By examining the phenotypes of family members, you can deduce the underlying genotypes and the mode of inheritance.
**Example:**
Consider a pedigree where a rare disorder is present in several individuals. You notice that the disorder appears to skip generations, suggesting a recessive inheritance pattern. Furthermore, you observe that affected individuals tend to have unaffected parents, indicating that the disorder is carried by the parents in a heterozygous state. Through careful analysis of the pedigree, you can determine the genotype of each individual and confirm the mode of inheritance.
2. Probability Calculations: Predicting the Future
Another common challenge in complex inheritance problems involves probability calculations. Given the genotypes of parents, you’re tasked with predicting the probability of their offspring inheriting specific phenotypes or genotypes. This requires a firm grasp of the principles of probability and the knowledge to apply them to the specific inheritance pattern in question.
**Example:**
Imagine a scenario where parents are both heterozygous for a polygenic trait, such as eye color. Each parent contributes one allele from each gene to their offspring. To calculate the probability of a child inheriting a specific eye color, you need to consider the possible combinations of alleles from each gene and their respective probabilities. This can involve using Punnett squares or other probability tools to determine the likelihood of different outcomes.
The Answer Key: Mastering the Language of Genetics
Here are some key steps to help you decode complex inheritance practice problems:
- Identify the trait and its mode of inheritance: Is it a single-gene trait or a polygenic trait? Is it dominant or recessive? Does epistasis play a role?
- Analyze the data: Examine pedigree charts or given information carefully. Note the phenotypes of individuals, their relationships, and any other relevant details.
- Use Punnett squares or other probability tools: Depending on the complexity of the problem, these tools can help visualize the possible genotype combinations and their probabilities.
- Consider environmental factors: In some cases, environmental influences can modify the expression of a trait, so it’s important to keep them in mind.
- Don’t be afraid to break down the problem: Complex inheritance challenges can be daunting. Focus on one aspect at a time, working through the steps systematically to unravel the puzzle.
The Power of Practice: Unlocking the Secrets of Inheritance
As with any skill, mastering complex inheritance problems requires practice. The more problems you solve, the more confident you’ll become in your understanding of the underlying principles. Engage with practice problems, study worked-out examples, and seek guidance when needed. With persistence and a willingness to learn, you’ll transform from a hesitant learner into an expert decoder of genetic patterns.
Beyond the Classroom: The Real-World Implications of Complex Inheritance
The concepts of complex inheritance aren’t merely abstract academic curiosities; they have profound real-world implications. For example, understanding complex inheritance patterns is essential for:
- Medicine: Diagnosing and treating genetic disorders often involves understanding multi-gene interactions and environmental factors. Complex inheritance patterns contribute to the variability of disease expression and severity, influencing treatment options and prognosis.
- Agriculture: Breeders leverage the principles of complex inheritance to improve crop yields, enhance disease resistance, and develop desirable traits in livestock.
- Evolution: The study of complex inheritance plays a crucial role in understanding how populations evolve and adapt to changing environments.
Complex Inheritance Practice Problems Answer Key
Continuing Your Journey: Exploring the Ever-Expanding World of Genetics
The world of inheritance is a vast and ever-evolving field. As you continue your journey into this fascinating realm, don’t hesitate to explore additional resources, engage in discussions with others, and embrace the challenges that come with tackling complex problems. The rewards of understanding the intricacies of inheritance are immense, providing a deeper appreciation for the beauty and complexity of life itself. So, take a deep breath, grab your practice problems, and let the journey of discovery begin!





