Remember those early chemistry classes where you first encountered the mysterious forces holding atoms together? It all started with the concept of chemical bonds, those invisible threads weaving together the fabric of molecules. But distinguishing between ionic and covalent bonds, two fundamental types, can be confusing even for seasoned students. That’s where a well-crafted worksheet comes in!
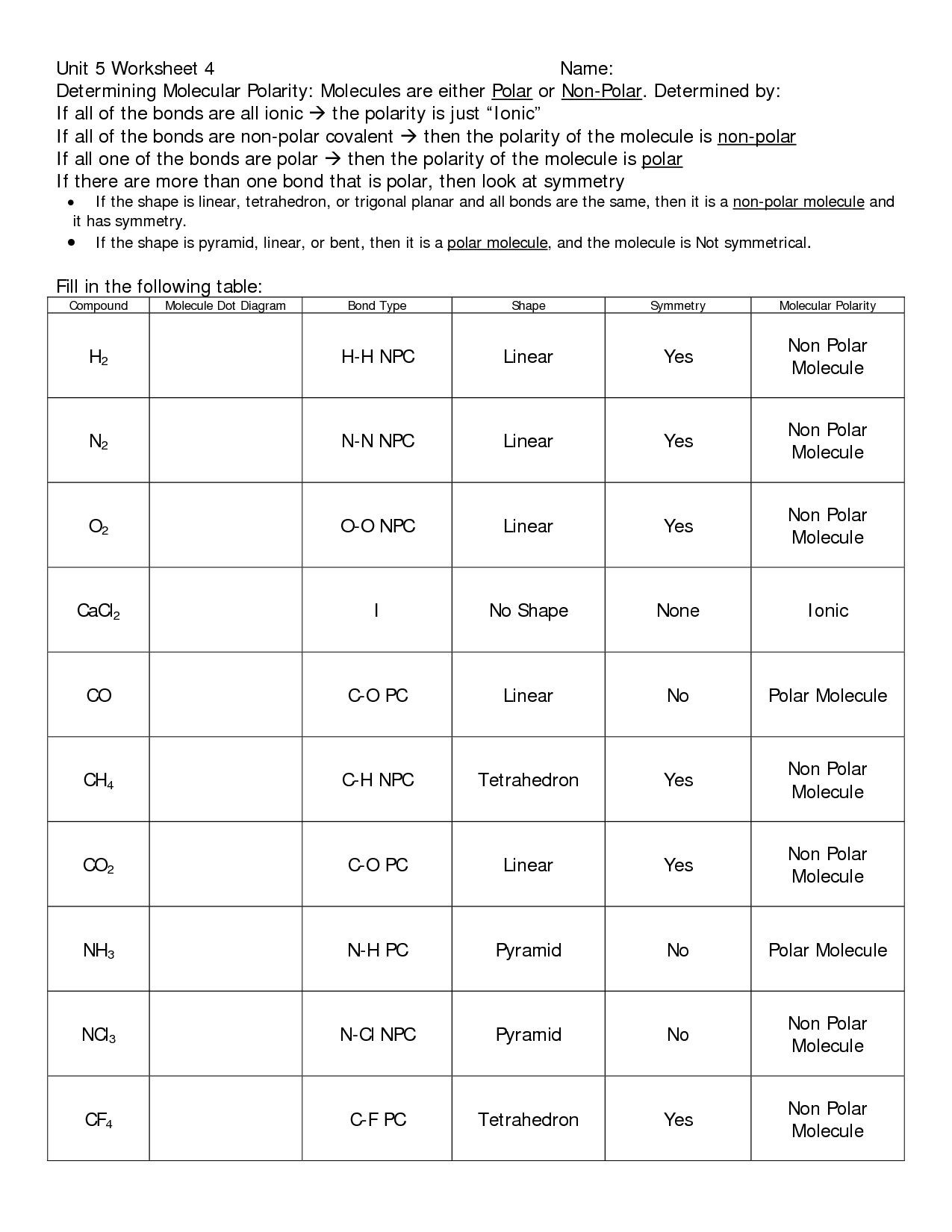
Image: www.worksheeto.com
As a tutor, I’ve witnessed countless students grapple with the intricacies of identifying these bonds. They’d diligently study the definitions and examples, but applying the knowledge to real-world scenarios often proved tricky. This is precisely where a thoughtfully designed worksheet, coupled with its answer key, acts as a vital guide. It’s like having a personal coach by your side, patiently explaining each step and demystifying the complexities of chemical bonding.
Understanding the Essence of Ionic and Covalent Bonds
Delving into the Fundamental Differences
The essence of a chemical bond lies in the sharing or transferring of electrons between atoms. In ionic bonds, electrons are transferred – one atom essentially “gives” an electron to another. This transfer creates charged particles called ions, which are then held together by electrostatic attraction. Imagine two magnets of opposite poles: they are drawn together by an invisible force! In covalent bonds, electrons are shared between two atoms. It’s like a collaboration: each atom contributes one or more electrons to form a shared pool. The resulting bond is characterized by a mutual “hold” on the electrons, leading to a stable molecule.
Factors Determining Bond Formation
Electronegativity, the measure of an atom’s tendency to attract electrons in a covalent bond, plays a crucial role. When the difference in electronegativity between two atoms is significant (greater than 1.7), an ionic bond results. But when the electronegativity difference is relatively small, a covalent bond prevails. Additionally, the number of valence electrons, those situated in the outermost shell of an atom, impacts the type of bond formed. Nonmetals, seeking to complete their octets by gaining electrons, often participate in ionic bonds, while metals, with their tendency to lose electrons, prefer covalent bonds.
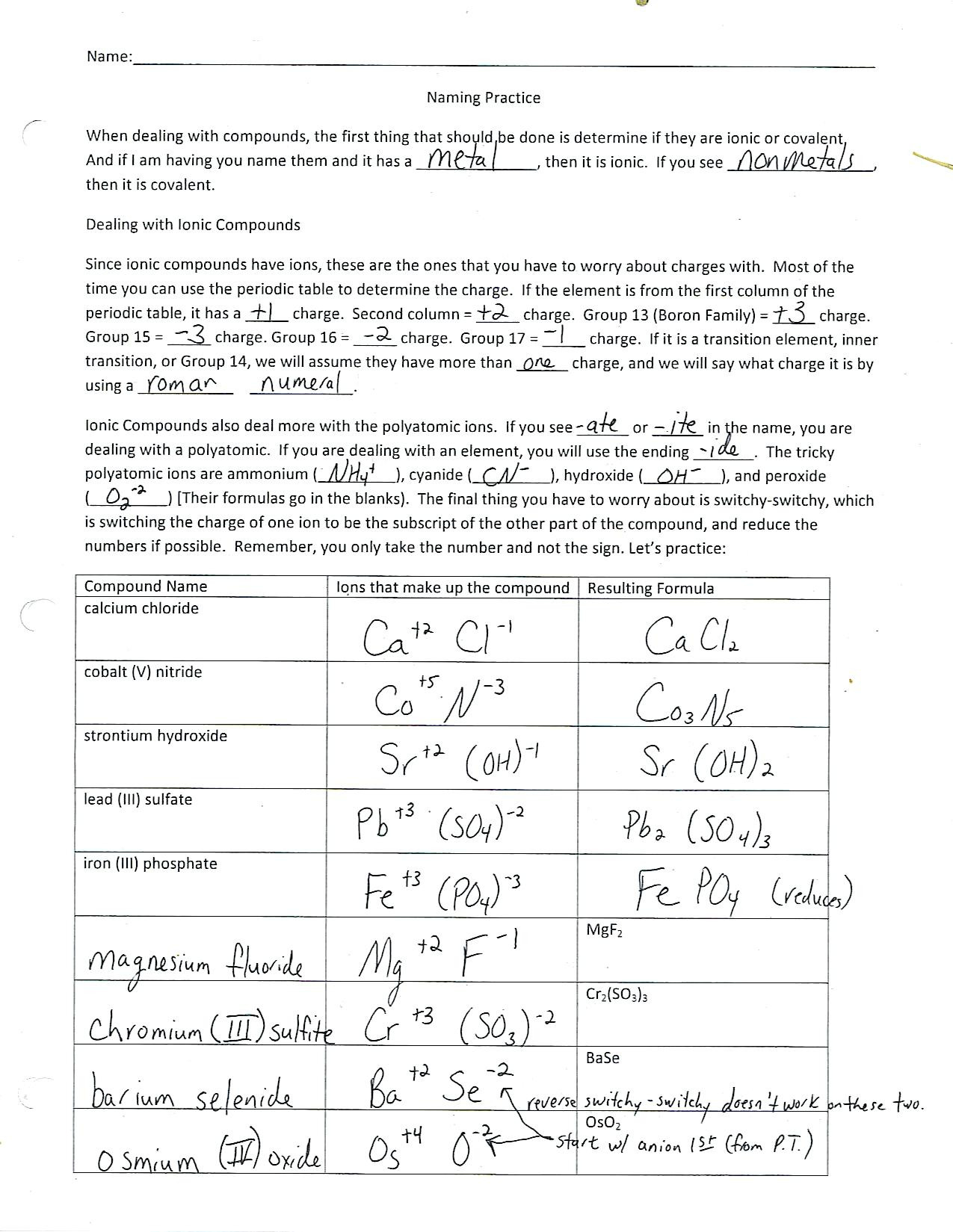
Image: materialcecilia.z13.web.core.windows.net
Unveiling the Clues for Identification
A worksheet designed to help students identify ionic and covalent bonds typically provides a set of molecules or compounds. Each entry presents a combination of elements, and the task is to determine the type of bond present within the molecule. This is achieved by considering the electronegativity difference between the participating elements. For instance, a large electronegativity difference between a metal and a nonmetal is a strong indicator of an ionic bond. Conversely, a small difference, especially between two nonmetals, generally points towards a covalent bond.
Mastering the Art of Identifying Bonds: A Step-by-Step Approach
1. **Identify the elements involved**: Begin by listing the elements forming the molecule or compound. This lays the foundation for analyzing their properties.
2. **Determine their positions on the periodic table**: Knowing the position of each element helps you deduce its electronegativity. Elements towards the right and top of the periodic table tend to be more electronegative than those towards the left and bottom.
3. **Calculate the electronegativity difference**: Refer to a reliable electronegativity table and find the values for the elements involved. Subtract the smaller value from the larger one to get the difference.
4. **Interpret the electronegativity difference**: If the difference is greater than 1.7, the bond is ionic. If it’s less than 1.7, the bond is covalent.
5. **Consider the nature of the elements**: While the electronegativity difference is a crucial indicator, it’s important to note that the nature of the elements themselves provide additional clues. Metal-nonmetal combinations often result in ionic bonds, while nonmetal-nonmetal combinations are more likely to form covalent bonds. This rule of thumb can serve as a helpful guide when interpreting the results of your analysis.
Top Tips for Conquering the Worksheet
As a seasoned chemistry tutor, I’ve observed that certain approaches work remarkably well for students. Here are some valuable tips to navigate the challenging world of ionic and covalent bond identification:
1. **Embrace the periodic table**: It’s your ultimate weapon! Understanding electronegativity trends and identifying elements’ positions on the table will drastically enhance your ability to predict bond types.
2. **Practice makes perfect**: The more you practice, the more comfortable you’ll become with the key concepts. Don’t hesitate to work through the worksheets multiple times, focusing on identifying the steps and reasoning behind your conclusions.
3. **Utilize online resources**: Utilize online tools, like electronegativity calculators and interactive worksheets, to solidify your understanding. These resources provide a visual aid and instant feedback, easing your learning journey.
Unraveling Common Misconceptions
1. **Ionic bonds are always between metals and nonmetals**: While this is generally true, there are exceptions. For instance, some metal-metal bonds exhibit significant ionic character. It’s crucial to consider individual examples and avoid overgeneralizations.
2. **Covalent bonds never have ionic character**: Though covalent bonds often involve sharing of electrons, the sharing isn’t always equal. In polar covalent bonds, one atom attracts the shared electrons more strongly, leading to a partial positive and a partial negative charge within the molecule. This adds a degree of ionic character to the bond.
FAQ: Addressing Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is a chemical bond?
A: A chemical bond is a force of attraction between two or more atoms that holds them together, forming a molecule. This force can arise from the sharing or transfer of electrons between the atoms.
Q: What are the major types of chemical bonds?
A: Two main types of chemical bonds exist: ionic bonds and covalent bonds. Ionic bonds involve the complete transfer of electrons, while covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons.
Q: How do I determine the type of bond between two atoms?
A: The primary factor influencing bond type is the difference in electronegativity between the two atoms. A large difference (greater than 1.7) suggests an ionic bond, while a small difference implies a covalent bond.
Identifying Ionic And Covalent Bonds Worksheet Answer Key
Conclusion
Identifying ionic and covalent bonds is a fundamental skill in chemistry. By systematically analyzing the electronegativity difference, focusing on the nature of the elements, and honing your problem-solving skills, you can confidently navigate worksheets, unraveling the mysteries of chemical bonds. Remember, practice is key! The more you engage with worksheets and explore real-world scenarios, the deeper your understanding will become. And remember, the journey of learning is never-ending. Are you ready to continue your chemical bonding adventure? Tell us in the comments below!





