Have you ever found yourself stranded on the side of the road, the engine sputtering, and the dashboard resembling a Christmas tree of warning lights? This frustrating scenario can happen to anyone, but for 2007 Dodge Caliber owners, understanding the fuse box layout could be the key to regaining control of your journey. Your car’s fuse box is a vital component, housing a network of fuses that protect the electrical circuits from overload and prevent potential fire hazards. By understanding how this system works, you can be prepared to handle any electrical malfunctions that arise!
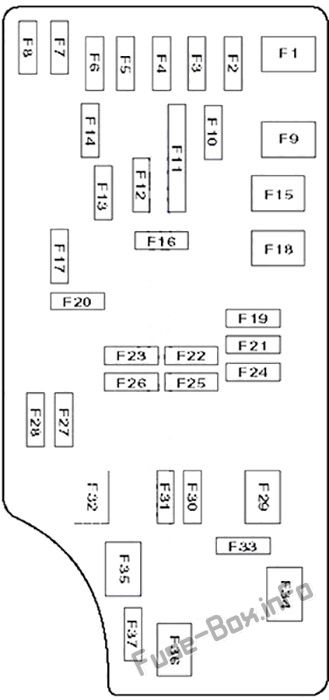
Image: flavored.ph
This guide will equip you with all the knowledge you need to navigate the intricate landscape of your 2007 Dodge Caliber’s fuse box. We’ll explore its layout, uncover the secrets of each fuse, and provide step-by-step instructions for safely replacing fuses. Let’s roll up our sleeves, get ready to learn, and conquer any electrical challenges that come your way.
Navigating the 2007 Dodge Caliber’s Fuse Box
The 2007 Dodge Caliber boasts two fuse boxes: one conveniently located inside the vehicle, and another tucked away under the hood. Let’s dive into the details of each location, revealing the essential information you need to tackle any electrical hiccups with confidence.
The Interior Fuse Box: A Quick and Easy Check
There’s a fuse box conveniently situated within your 2007 Dodge Caliber’s passenger cabin, making it easily accessible for those essential checks. This box, usually found on the driver’s side of the dashboard, houses fuses for various components, including the lighting, power windows, and other interior features.
1. Location: The interior fuse box is typically found under the dashboard on the driver’s side.
2. Access: To access the fuse box, you’ll need to first locate the fuse box cover. It may be secured with a latch, clip, or simply held in place by a few screws. Once you’ve removed the cover, you’ll be greeted with the array of fuses, labeled for easy identification.
3. Identifying Fuses: Each fuse is clearly labeled with its corresponding circuit and amperage. This means you can easily pinpoint the fuse responsible for a specific component; if a particular device is acting up, a quick glance at the fuse box can tell you if the fuse has blown. Remember: if you notice a blown fuse, always replace it with a fuse of the same amperage. Using a fuse with a different amperage can damage your car’s electrical system.
The Under-the-Hood Fuse Box: Powering the Engine’s Functions
Under the hood, nestled near the battery, lies another crucial fuse box. This powerhouse handles the electrical demands of your engine, from ignition to the fuel pump, ensuring everything runs smoothly.
1. Location: The under-the-hood fuse box is typically located near the battery, on the driver’s side of the engine compartment.
2. Access: To access the under-the-hood fuse box, you’ll often need to remove a plastic cover that secures the fuse box. This cover may be held in place with clips or screws.
3. Identifying Fuses: Similar to the interior fuse box, the under-the-hood fuse box has clearly labeled fuses with their amperage. Keep a watchful eye on this box, as any blown fuses within could cause significant complications for your car’s performance.

Image: www.vrogue.co
Understanding Fuse Types and Their Role
Fuses play a critical role in protecting your car’s electrical system from overloads and damage. But did you know there are different types of fuses? Let’s delve into the world of fuses and their unique characteristics:
1. Blade Fuses: These are a common type of fuse found in most modern vehicles, including your 2007 Dodge Caliber. They feature a small, rectangular blade with contacts on either end, and are typically designed for low amperage circuits.
2. Cartridge Fuses: Cartridge fuses are cylindrical in shape and are often used for higher amperage circuits, like those powering the engine. They have a threaded base that secures them into the fuse box.
3. Glass Fuses: These fuses are typically used for older vehicles and feature a glass body with a thin wire element inside. When the wire element melts due to an overload, the fuse breaks the circuit, preventing further damage.
The Importance of the Fuse Box: A Safety Net for Your Electrical System
The fuse box may seem like a mundane part of your car, but it plays a vital role in ensuring the safety and reliability of your electrical system. Here’s why you should never underestimate the importance of your fuse box:
1. Overcurrent Protection: Fuses act as a safety device, preventing overloads in electrical circuits. When a circuit draws more current than it’s designed for, the fuse melts, breaking the circuit and preventing potential damage to wires, components, and even fires.
2. Circuit Isolation: Fuses isolate specific electrical circuits within your car. This means if a fuse blows, you can quickly identify the affected circuit and isolate it from the rest of the electrical system. This makes troubleshooting any electrical issues much easier.
3. Preventing Fires: A blown fuse may seem like a minor inconvenience, but it could prevent major damage or even a fire. Faulty wiring or electrical components can draw excessive current, potentially causing a fire. Fuses ensure that even in such cases, the overload is safely broken, mitigating the risk of fire.
Replacing a Blown Fuse: A Simple DIY Task
Replacing a blown fuse is a simple DIY task that even novice car owners can perform. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get it right:
-
Identify the Blown Fuse: Visually inspect the fuse box and look for a fuse with a broken or melted wire element. You may also notice the fuse has a visible gap between the contacts.
-
Pull Out the Blown Fuse: Use a fuse puller to gently remove the blown fuse from its slot. A fuse puller is a small, specialized tool designed for this purpose.
-
Select a Replacement Fuse: Before replacing the fuse, make sure you have a new fuse with the same amperage rating as the blown fuse.
-
Insert the New Fuse: Use the fuse puller to carefully insert the new fuse into the empty slot. Make sure the fuse is properly seated.
-
Test the System: After replacing the fuse, test the related system to ensure it’s working properly. If the problem persists, the issue may be more complex, and you may need to seek assistance from a qualified mechanic.
The Importance of a Properly Labeled and Organized Fuse Box
A well-organized fuse box is not just about aesthetics. It’s a vital tool for easy troubleshooting and efficient repairs. Here’s why proper labeling is crucial:
1. Quick Identification: A properly labeled fuse box allows you to instantly identify the fuse responsible for a specific component. This can save you countless hours of troubleshooting and frustration.
2. Safe Replacement: By accurately knowing the amperage of each fuse, you can ensure you replace it with the correct one, minimizing the chance of damage to your car’s electrical system.
3. Easy Maintenance: A labeled fuse box facilitates routine checks and maintenance. You can quickly scan for any blown fuses and replace them before they cause further problems.
Beyond the Basics: Addressing Electrical Dilemmas
While replacing a blown fuse solves many electrical issues, more complex problems might require further exploration. Always remember that safety comes first! If you’re not comfortable working with electrical systems, it’s best to consult a qualified mechanic. However, here are some common issues and ways to troubleshoot them:
1. Power Window Problems: If your power windows are not working, first check the corresponding fuse in the interior fuse box. If the fuse is blown, replace it, and then try the windows again.
2. Electrical System “Glitch”: If you experience unusual electrical behavior, like intermittent flickering lights or inconsistent performance of certain features, it’s a good idea to start with the fuse boxes and check for any blown fuses. Remember, a blown fuse might be a symptom of a larger issue, so it’s wise to consult a mechanic if you notice persistent or recurring problems.
3. Engine Problems: A blown fuse in the under-the-hood fuse box could lead to various engine problems. You may encounter difficulties starting the engine, notice a lack of power, or experience issues with the fuel pump, which could be indicated by a persistent check engine light.
2007 Dodge Caliber Fuse Box Layout
Empowering You to Take Charge of Your 2007 Dodge Caliber
Armed with the knowledge of your 2007 Dodge Caliber’s fuse box layout, you’re equipped to handle minor electrical issues with confidence. Remember, a well-maintained fuse box is an essential part of keeping your car running smoothly and safely. From identifying blown fuses to performing basic replacements, understanding this crucial component empowers you to stay in control of your journey. So next time you face an electrical issue, don’t panic! Remember the fuse box and its vital role in keeping your car running smoothly.





