Have you ever wondered why a seesaw teeters back and forth, or why a car accelerates when you press the gas pedal? The answer lies within the fascinating world of forces, specifically the concepts of balanced and unbalanced forces.
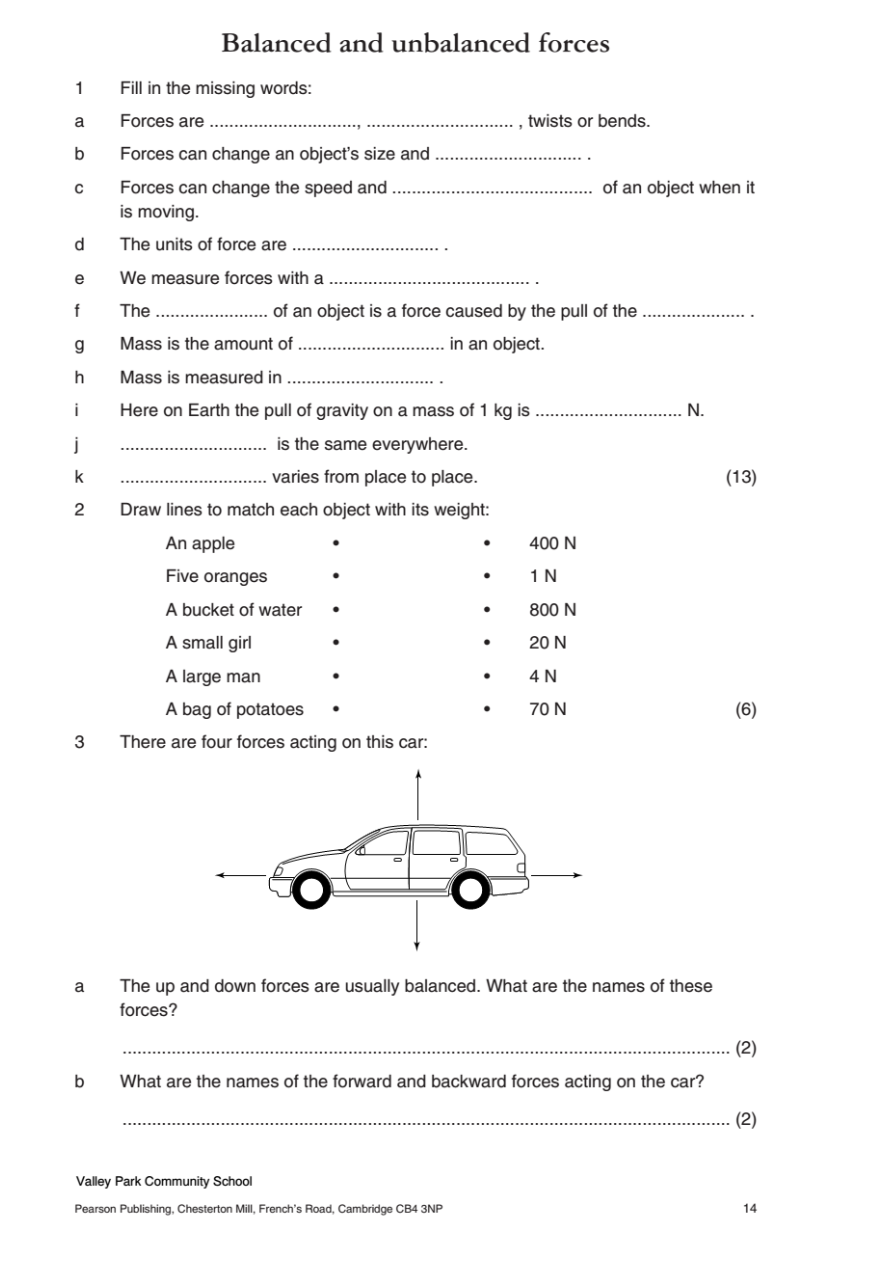
Image: www.evolvingsciences.com
Understanding these concepts is crucial for comprehending how objects move and interact with each other. This guide will delve into the intricacies of balanced and unbalanced forces, exploring the fundamentals, real-world applications, and providing you with comprehensive worksheet answers to solidify your understanding.
Defining Forces: The Building Blocks of Motion
Before diving into the specifics of balanced and unbalanced forces, let’s first establish a solid understanding of forces themselves. A force is simply a push or pull that can alter an object’s motion or shape. Forces have both magnitude (strength) and direction, which are crucial factors in determining their effects.
Imagine a child pushing a toy car across the floor. The child exerts a force on the car, causing it to move. This force has a magnitude (the amount of push) and a direction (the way the child pushes). Similarly, when you lift a heavy box, you apply an upward force to counteract gravity’s downward pull.
Balanced Forces: A State of Equilibrium
In the realm of forces, a state of balance occurs when the net force acting on an object is zero. In simpler terms, this means all the forces acting on the object are perfectly cancelling each other out. When balanced forces are at play, an object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion continues moving at a constant velocity.
Consider a book resting on a table. The book experiences two forces: gravity pulling it downwards and the table pushing it upwards. These forces are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction, resulting in a net force of zero. Therefore, the book remains still, a prime example of balanced forces in action.
Unbalanced Forces: The Drivers of Motion
Unbalanced forces, as you might expect, are the antithesis of their balanced counterparts. They occur when the net force acting on an object is not zero, meaning the forces are not perfectly canceling each other. Unbalanced forces are the catalysts that cause objects to accelerate, either speeding up, slowing down, or changing direction.
Imagine a soccer player striking the ball. The player’s foot imparts a force to the ball, causing it to accelerate forward. This force is greater than the force of friction acting on the ball, resulting in an unbalanced force that propels the ball across the field.

Image: answercampusholtzmann.z19.web.core.windows.net
Impact of Balanced and Unbalanced Forces on Motion
The interplay of balanced and unbalanced forces dictates the behavior of objects. Here’s a breakdown of their key effects:
Balanced Forces:
- No Change in Motion: Balanced forces result in no change in an object’s velocity. If an object is at rest, it will remain at rest. If it’s in motion, it will continue moving at a constant speed in a straight line.
Unbalanced Forces:
- Acceleration: Unbalanced forces cause acceleration, meaning a change in an object’s velocity. This could be an increase in speed, a decrease in speed, or a change in direction.
Illustrative Examples: Bringing Forces to Life
Let’s look at some real-world examples to solidify our understanding of balanced and unbalanced forces:
Example 1: The Seesaw
A seesaw is a classic illustration of balanced and unbalanced forces. When two children of equal weight sit on opposite ends of the seesaw, the forces they exert are balanced. The seesaw remains level, and neither child moves up or down. However, if one child is heavier than the other, the forces become unbalanced. The heavier child will push the seesaw down, and the lighter child will be lifted up. This change in motion is a direct result of unbalanced forces.
Example 2: A Car in Motion
When a car is at rest, the forces acting on it are balanced. Gravity pulls the car downwards, while the ground pushes it upwards with an equal force. This keeps the car stationary. However, when the driver presses the gas pedal, the engine applies a forward force. This force is greater than the forces of friction resisting the car’s movement, resulting in an unbalanced force that causes the car to accelerate forward.
Mastering the Concepts: Worksheet Answers
To solidify your understanding of balanced and unbalanced forces, we’ve compiled a set of worksheet answers that cover key concepts and scenarios. These answers will help you grasp the fundamental principles and apply them to real-world situations.
Worksheet Answers:
- Scenario 1: A book is sitting on a table. What forces are acting on the book, and are they balanced or unbalanced?
- Answer: The book is subject to two forces: gravity pulling it downwards and the table pushing it upwards. These forces are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction, making them balanced forces. Therefore, the book remains at rest.
- Scenario 2: A child pushes a toy car across the floor. Is the car experiencing balanced or unbalanced forces?
- Answer: The child’s push is an unbalanced force, as it’s greater than the force of friction acting on the car. This unbalanced force causes the car to accelerate forward.
- Scenario 3: A ball is thrown into the air. Describe the forces acting on the ball as it rises and falls.
- Answer: When the ball is thrown upwards, it experiences gravity pulling it downwards and air resistance slowing it down. These forces, initially unbalanced, cause the ball to slow down as it rises. At the peak of its trajectory, the forces momentarily balance, and the ball briefly stops moving. As the ball falls, gravity pulls it downwards, and air resistance continues to act on it. These forces, again unbalanced, cause the ball to accelerate downwards.
Exploring Further: Expanding Your Horizons
Understanding balanced and unbalanced forces opens doors to a captivating world of physics. To delve deeper, consider exploring these avenues:
- Newton’s Laws of Motion: These laws provide a foundational framework for understanding how forces affect motion.
- Friction: Learn about the different types of friction and how it impacts motion.
- Gravity: Explore the force that keeps us grounded and influences the motion of celestial bodies.
- Real-World Applications: Investigate the practical applications of balanced and unbalanced forces in engineering, transportation, and other fields.
Balanced And Unbalanced Forces Worksheet Answers Pdf
Conclusion
By grasping the concepts of balanced and unbalanced forces, we gain a deeper understanding of how objects move and interact in our world. Whether it’s pushing a toy car, riding a bicycle, or launching a rocket, the principles of forces are at play. This knowledge empowers us to solve problems, design innovative solutions, and appreciate the intricate beauty of the physical world.





