Imagine walking into a patient’s room, a space filled with unspoken emotions and complex needs. You, as a psychiatric nurse, navigate the conversation, offering empathy and support, but also meticulously documenting every interaction, every flicker of emotion. This is the world of process recording, a powerful tool in psychiatric nursing that allows us to reflect, analyze, and improve our therapeutic practice.

Image: www.youtube.com
Process recording goes beyond simply writing down what happened in a patient encounter. It involves capturing the nuances of the interaction, including your own feelings, thoughts, and reactions. It helps you to delve deeper into the complexities of the therapeutic relationship, fostering self-awareness and improved care for your patients.
The Essential Elements of Process Recording
Understanding the Basics
Process recording, often referred to as a “therapeutic log,” is a written account of a therapeutic interaction between a nurse and a patient. It serves as a valuable tool for nurses to analyze their communication, identify patterns, and enhance their therapeutic skills. The ultimate goal is to improve the quality of care provided to patients by promoting reflection and critical thinking.
The Components of a Process Recording
A process recording typically includes the following elements:
- Patient Information: Basic details about the patient, such as age, diagnosis, and reason for seeking care.
- Date and Time: Clearly noting the time and date of the interaction.
- Setting: Where the interaction took place, like a patient’s room or a group therapy session.
- Patient’s Verbal and Nonverbal Communication: Detailed documentation of the patient’s words, tone of voice, facial expressions, and body language.
- Nurse’s Verbal and Nonverbal Communication: A comprehensive record of your own words, tone, and non-verbal cues.
- Nurse’s Thoughts and Feelings: Honest reflection on your personal reactions to the patient’s words and behaviors, including any biases or assumptions.
- Therapeutic Techniques: Listing the specific therapeutic interventions used, such as active listening, empathy, or challenging maladaptive beliefs.
- Analysis: Interpreting the interaction, identifying patterns, and drawing conclusions about the patient’s emotional state and therapeutic progress.
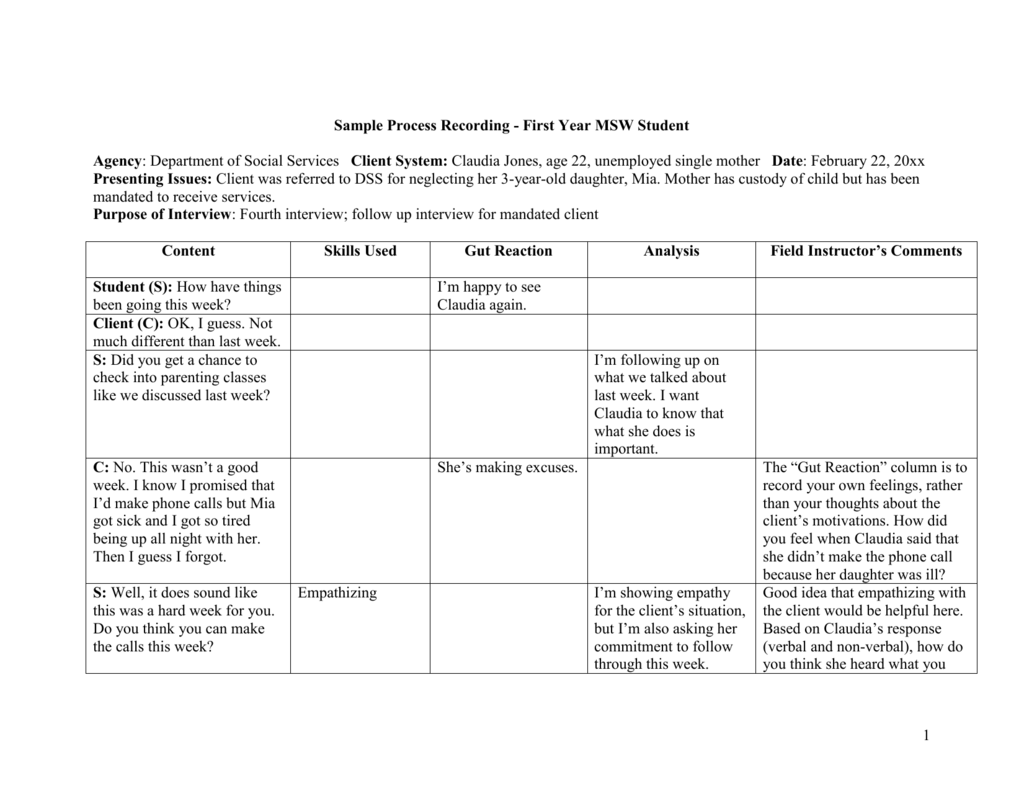
Image: template.mapadapalavra.ba.gov.br
The Value of Process Recording
Process recording offers numerous benefits for both nurses and patients:
- Enhanced Therapeutic Skills: It helps nurses to develop and refine their communication, empathy, and active listening skills.
- Improved Self-Awareness: By examining their responses and reactions, nurses gain a deeper understanding of their own biases and how they might impact patient interactions.
- Better Patient Understanding: Process recording facilitates a more in-depth analysis of patient behavior, promoting a deeper understanding of their emotional needs and underlying issues.
- Enhanced Communication: It encourages nurses to be more mindful of their communication style and to use language that is clear, concise, and therapeutic.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Process recordings can be shared with other healthcare professionals, facilitating a collaborative approach to patient care.
- Improved Patient Outcomes: Through reflective learning and enhanced therapeutic skills, process recording contributes to improved patient care and outcomes.
Process Recording Sample: A Glimpse into Practice
“Patient: ‘I feel so alone. Nobody understands what I’m going through.’
Nurse: ‘It sounds like you’re feeling very isolated and misunderstood. Would you like to talk about what’s making you feel this way?’
Nurse’s Thoughts: I felt empathy for the patient’s feelings of loneliness. I want to create a safe space for them to share, but I’m unsure how to approach this sensitive topic without overwhelming them.”
This excerpt from a process recording demonstrates how nurses capture both the patient’s verbal communication and their own thoughts and feelings. The nurse’s reflection allows them to analyze their response and potentially adjust their approach in future interactions.
Tips for Effective Process Recording
To maximize the benefits of process recording, here are some key tips:
- Regular Practice: Make it a habit to record interactions regularly, even briefly, to develop this skill.
- Focus on the Therapeutic Relationship: Remember to document the interaction from a therapeutic lens, focusing on the dynamics between you and the patient.
- Be Honest and Descriptive: Record your thoughts and feelings honestly, even if they are negative or difficult to confront.
- Practice Reflective Analysis: Take time to analyze the interaction, looking for patterns and identifying areas where you could improve.
- Utilize Feedback: Share your process recordings with a supervisor or colleague for feedback and professional development.
FAQ: Addressing Common Questions
Q: What are the ethical considerations surrounding process recording?
A: It’s crucial to maintain patient confidentiality. Only share recordings with other professionals involved in their care and make sure any identifiable information is concealed. The primary focus is on the therapeutic process, not judgment or gossip.
Q: How often should I engage in process recording?
A: The frequency depends on the setting and your experience. For new nurses or challenging cases, a daily record could be helpful. Even brief recordings can be beneficial for reflective learning.
Q: How do I find time for process recording?
A: Plan for dedicated time, even if it’s just 15 minutes after an interaction. You can even record key points on a sticky note during the encounter and expand on it later.
Q: Is it okay to use process recording as a way to “vent” about challenging patients?
A: No. Process recording is about professional growth, not personal venting. Focus on analyzing the interaction from a therapeutic perspective, rather than expressing frustrations.
Process Recording Sample In Psychiatric Nursing
Conclusion: Embracing Reflection in Psychiatric Nursing
Process recording is a powerful tool for psychiatric nurses, enabling us to deepen our understanding of our patients and ourselves. By regularly engaging in reflective practice, we can continue to enhance our therapeutic skills, promote collaboration with colleagues, and ultimately provide the best possible care for our patients.
Do you find process recording to be a valuable tool in your practice? Share your experiences and insights in the comments below!





