The concept of a single party system might seem alien to many readers accustomed to democratic systems where multiple parties compete for power. However, it’s a reality for a significant portion of the globe. In countries like China, Vietnam, and Cuba, a single party holds the reins of power, shaping the political landscape and dictating the course of the nation. As I traveled through Vietnam a few years back, I couldn’t help but be captivated by the country’s unique political structure. Seeing the omnipresent influence of the Communist Party, from the local government to the national stage, sparked my curiosity about the advantages and disadvantages of such a system.

Image: www.tutorialandexample.com
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the single party system, delving into its historical context, its perceived advantages and disadvantages, and its place in the world today. We’ll explore the complexities of this political model, examining the arguments for and against it, and analyzing its implications for governance, human rights, and economic development.
What is a Single Party System?
A single party system is a political structure where a singular political party holds the dominant position in the government, excluding or significantly limiting the participation of other parties. This system often entails centralized control, with the ruling party wielding extensive power over various aspects of the nation, including the legislature, judiciary, and media. While there might be other parties present, their influence is typically minimal, either through a lack of electoral opportunity or limitations on their activities.
Historically, single-party systems have emerged in various contexts, including post-revolutionary periods, like in China after the communist revolution, or in countries transitioning from colonialism, such as Vietnam, where a unified political force was perceived as crucial for national development. The prevalence of single-party systems in communist or socialist states further reinforces this association.
Advantages of a Single Party System
1. Stability and Continuity
A single party system can, in theory, offer stability and continuity. Without the constant shifting of power and policy changes that can accompany multi-party systems, the ruling party can implement long-term plans and initiatives without fear of being challenged or disrupted by opposing political forces. This can be particularly appealing in countries experiencing political instability or transitioning from conflict.
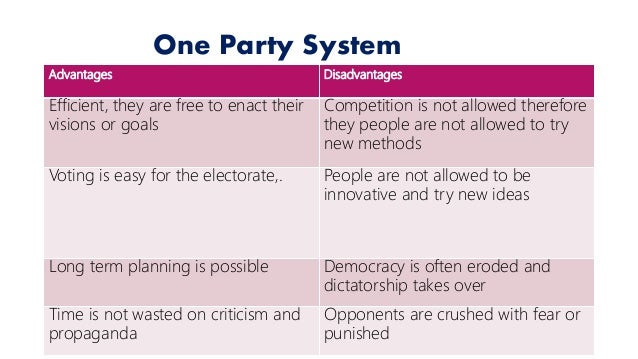
Image: www.slideshare.net
2. Focused Development
With a singular vision and a consolidated power structure, a single party system can potentially prioritize and implement development policies with greater efficiency. Without the need to accommodate or compromise with diverse viewpoints, the party can focus on targeted goals and allocate resources effectively to achieve them. This can be observed in countries experiencing rapid economic growth under single-party rule, where infrastructure projects, industrialization, and other development initiatives are driven forward with a clear sense of direction.
3. National Unity and Cohesiveness
Single party systems often espouse a strong sense of national unity and cohesion. The central party can promote a shared ideology, history, and cultural identity, fostering a sense of belonging and collective purpose among citizens. This can be particularly advantageous in countries with diverse ethnicities, religions, or regional identities, where a unified political front can help to maintain stability and prevent conflict.
Disadvantages of a Single Party System
1. Lack of Political Competition
The most significant drawback of a single party system is the lack of genuine political competition. Without a system of checks and balances, the ruling party can become entrenched, leading to corruption, a lack of accountability, and diminished responsiveness to public concerns. The absence of meaningful opposition can also stifle innovation and hinder progress, as the party’s ideas and policies may remain unchallenged.
2. Suppression of Dissent and Human Rights
Single party systems often have a history of suppressing dissent and limiting individual liberties. The ruling party may use its control over the media, law enforcement, and judiciary to silence critics, restrict free speech, and curtail the right to assemble. This can lead to a culture of fear and conformity, hindering the development of a vibrant and critical civil society.
3. Economic Inequity and Corruption
A lack of transparent governance and accountability in single party systems can lead to economic inequality and corruption. The ruling party may prioritize its own interests and those of its supporters, leading to the concentration of wealth and power in the hands of a select few. This can create social unrest and undermine the long-term stability of the system.
The Single Party System in a Global Context
While single-party systems remain widespread, their influence is not without its challenges. The rise of globalization and the interconnectedness of economies has forced even single-party states to engage with the global market, often leading to a compromise between their own political systems and the demands of international trade and investment. Additionally, the spread of information and communication technologies has made it increasingly difficult for single-party regimes to control the flow of information and suppress dissent.
The continued existence of single-party systems is a complex issue with both internal and external factors playing a role. Some argue that the continued presence of these systems speaks to their inherent advantages, while others maintain that it is a testament to the lack of viable alternatives.
Tips and Expert Advice
For those interested in understanding the dynamics of single-party systems, here are some tips and expert advice:
- Engage with primary sources: Seek out information directly from countries governed by single-party systems, including official statements, government documents, and independent media outlets. This will give you a more nuanced understanding of the perspectives within these societies.
- Focus on specific case studies: Explore individual countries with single party systems, comparing their political, social, and economic structures to understand the unique challenges and opportunities they face. This will provide a more in-depth analysis than simply generalizing across all single party states.
- Consider the historical context: Understand the circumstances surrounding the rise of single-party systems, examining the historical and political factors that led to their emergence. This context will provide valuable insight into the motivations and rationale behind their development.
By engaging with these sources and approaches, readers can avoid generalizations and delve into the complexities of each case, gaining a more nuanced and informed perspective on single-party systems around the world.
FAQ
Here are some frequently asked questions about single-party systems:
- **What are some examples of countries with single-party systems?** Some well-known examples include China, Vietnam, Cuba, Laos, North Korea, and the former Soviet Union.
- **Is a single-party system always a bad thing?** Not necessarily. While many perceive single-party systems as inherently oppressive, some argue that they can provide stability and continuity, particularly in countries with a history of political instability.
- **How do single-party systems typically maintain their power?** Various methods are employed, including controlling the media, limiting the activities of opposition parties, and using propaganda to promote a specific ideology. Many also maintain a strong security presence and can resort to repression against dissent.
- **Is it possible for a single-party system to transition to a democratic system?** While a challenging process, it’s not impossible. Some countries have transitioned from single-party systems to multi-party democracy, but it often requires significant political reforms, a robust civil society, and international support.
Single Party System Advantages And Disadvantages
Conclusion
Exploring the topic of the single-party system reveals a complex political structure with both potential advantages and significant disadvantages. Understanding the various arguments for and against this system, alongside examining its implications for governance and human rights, is crucial for forming an informed perspective on this prevalent political model.
Have you ever lived in or visited a country with a single party system? What are your thoughts on the topic? Share your experiences and perspectives in the comments section below.





