Have you ever looked at the intricate web of wires connecting your air conditioner’s outdoor unit and felt a sense of bewilderment? You’re not alone! Most homeowners are unfamiliar with the AC outdoor unit wiring diagram, leaving them feeling helpless when faced with a malfunctioning system. This guide will demystify this essential component of your AC system, empowering you to understand its intricacies and confidently troubleshoot potential issues.
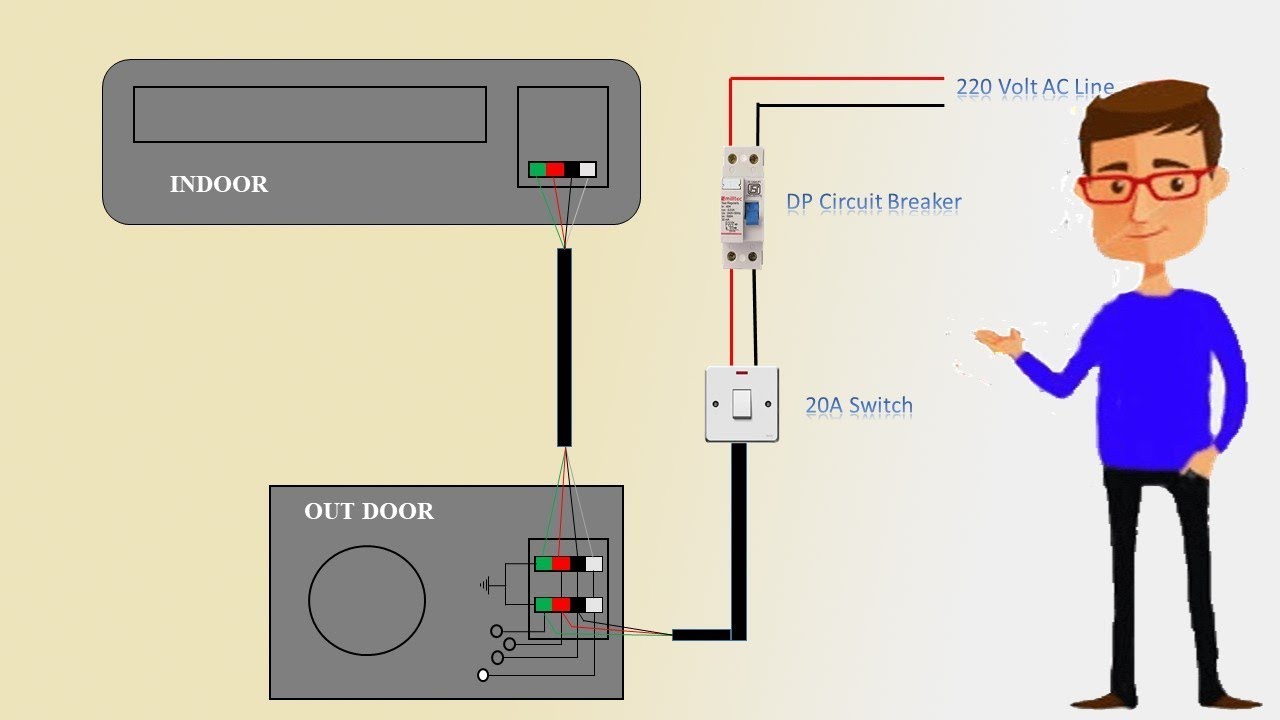
Image: mydiagram.online
The AC outdoor unit wiring diagram is a crucial tool for understanding the electrical connections within your air conditioner’s external unit. This diagram serves as a blueprint, visually representing the flow of electricity through various components, such as the compressor, fan motor, and control board. A comprehensive understanding of this diagram can help you diagnose problems, perform basic maintenance, and even replace faulty parts, all without calling a technician.
Understanding the Basic Components
Before diving into the details of the wiring diagram, let’s break down the key components of an AC outdoor unit:
Compressor: This powerful heart of the system condenses refrigerant, transferring heat from inside your home to the outside.
Condenser Fan Motor: This motor powers the condenser fan, responsible for drawing air across the condenser coils, facilitating heat dissipation.
Control Board: This electronic brain monitors and regulates the entire AC system, orchestrating the actions of other components.
Fan Relay: This component acts as a switch, controlling the flow of electricity to the condenser fan motor.
The Wiring Diagram Explained: A Step-by-Step Guide
Now, let’s explore the typical AC outdoor unit wiring diagram, focusing on the most common components and connections:
1. Power Supply: The main power supply line enters the outdoor unit, typically through a dedicated circuit breaker. This supply line usually consists of three wires: hot (black), neutral (white), and ground (green or bare copper).
2. Compressor: The hot wire from the power supply often directly connects to the compressor. A separate ground wire ensures safe operation. Specific wire sizes and terminal locations can vary based on the compressor’s model.
3. Condenser Fan Motor: The condenser fan motor receives power from the control board, typically through a relay. This allows the system to regulate fan speed based on cooling demands. A separate ground wire is essential for safety.
4. Control Board: The control board receives power from the power supply line. It also connects to the compressor, fan motor, and potentially other components, such as a thermostat. The control board monitors the system, ensuring proper operation and triggering alarms if necessary.
5. Thermostat: The thermostat sends signals to the control board, instructing it to start or stop the cooling cycle based on set temperature settings.
Reading the Diagram: Key Symbols and Color Codes
Understanding the symbols and color codes used in wiring diagrams is essential for proper interpretation. Here’s a breakdown of the common elements:
Color Codes:
- Black: Hot wire
- White: Neutral wire
- Green or Bare Copper: Ground wire
Symbols:
- Wires: Different line thickness can indicate different wire gauges (thickness). Arrows may indicate the direction of current flow.
- Terminals: Circles, rectangles, or other shapes represent connection points. Numbers or letters may indicate specific terminal locations.
- Components: Icons representing the compressor, fan motor, control board, and other parts.

Image: life-improver.com
Troubleshooting with the Wiring Diagram: A Practical Approach
By carefully examining the wiring diagram and understanding the connections, you can identify potential issues in your AC system:
- Loss of Power: Check the circuit breaker and the connection points for loose wires or blown fuses.
- Compressor Issues: Observe the compressor for signs of running or shutting down intermittently. Check the connections to and from the compressor.
- Condenser Fan Problems: Inspect the fan motor for signs of damage or burnt-out windings. Verify the fan relay is functioning properly. Check the fan’s blades for obstructions.
- Control Board Malfunction: Look for flashing LEDs on the control board, indicating potential error codes. Check the wiring connections to the control board.
Expert Insights: Tips from Professionals
Always prioritize safety when working with electrical components. Wear appropriate safety gear, including rubber-soled shoes and insulated gloves. If you’re uncomfortable with any aspect of troubleshooting or repairs, consult a qualified HVAC technician.
A C Outdoor Unit Wiring Diagram
Conclusion: Empowering Yourself to Maintain Your AC System
By understanding the AC outdoor unit wiring diagram, you take a significant step towards becoming a more informed homeowner. This knowledge empowers you to troubleshoot minor issues, potentially prolong the life of your system, and save on costly repair bills. Remember to consult a qualified professional for complex repairs and always prioritize safety above all else.





