Have you ever found yourself saying, “I’m going to visit Paris next year,” or “I’m going to start writing a novel?” If so, you’ve used the future tense with “going to,” a common and versatile grammatical structure in the English language. This simple phrase allows us to express our intentions, predictions, and plans for the future. It’s a powerful tool that can make our plans feel more concrete and achievable. But beyond its practical application, the use of “going to” reveals a fascinating glimpse into how we perceive and communicate about the future.

Image: www.studocu.com
The “going to” construction has permeated our everyday communication. Whether we’re talking about our personal aspirations, work projects, or even the upcoming weather, “going to” is a reliable way to signify what we expect to happen in the future. But as we delve deeper into the intricacies of this grammatical structure, we’ll discover that its usage goes beyond a simple expression of future events. It reflects our hopes, desires, and even our level of commitment to our future plans.
Understanding “Going To” in the Future Tense
Defining the “Going To” Structure
The “going to” future tense is formed by combining the verb “to be” (in the present tense) with the verb “to go” and the infinitive form of the main verb. For example, “I am going to eat” or “They are going to travel.” This construction is generally used to express future actions that are planned, intended, or predicted.
History and Evolution
The “going to” structure has a long history in the English language, dating back to the 16th century. Initially, it was used primarily to express a future intention or purpose. Over time, however, its usage expanded to include predictions and statements about future events that are considered likely to occur. This evolution reflects the changing ways in which people have viewed and communicated about the future.
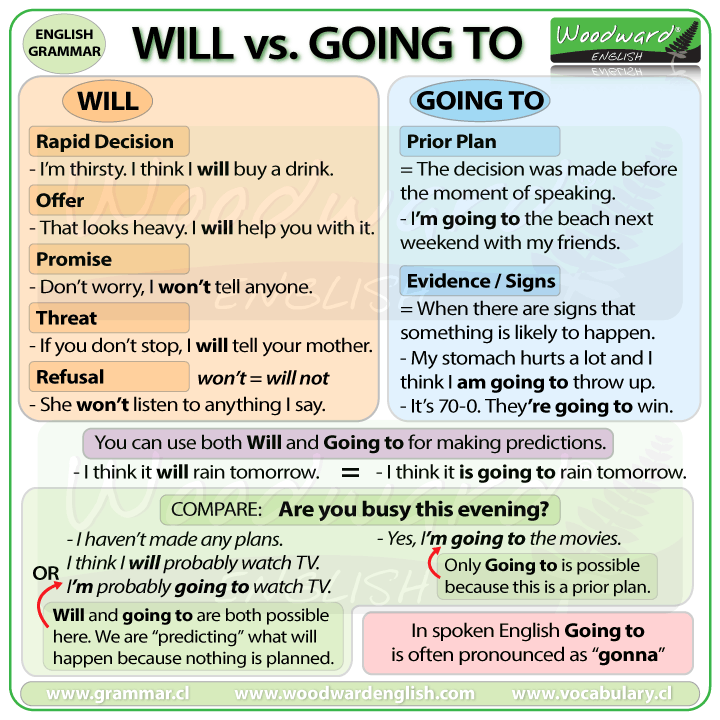
Image: www.grammar.cl
Meaning and Usage
The “going to” future tense is often used to express a sense of certainty or conviction about a future event. When someone says, “I am going to buy a new car,” they imply that they have made a decision and are committed to taking action. This contrasts with other ways of expressing the future, such as the simple future tense (“I will buy a new car”), which can convey a greater sense of uncertainty or possibility.
The “going to” structure can also be used to express future events that are not necessarily planned but are strongly predicted or anticipated. For instance, “It is going to rain tomorrow” suggests that there is a high likelihood of rain, based on current weather conditions or forecasts. In these cases, the phrase “going to” functions as a way to express a strong expectation or belief about the future.
Beyond Grammatical Structure: The Psychology of “Going To”
The use of “going to” goes beyond simple grammar. It reflects our intentions, our level of commitment to future plans, and even our perception of time. When we say “I’m going to graduate next year,” we’re not just stating a fact but also revealing our determination to achieve that goal. This subtle but powerful aspect of the language allows us to convey more than just information; it reflects our inner desires and aspirations.
The Role of Intention
One key role of “going to” is to convey intention. When we use it to express future plans, we’re essentially making a statement about our commitment to doing something. This commitment can be subtle or explicit, depending on the context. For example, “I’m going to visit my parents this weekend” implies a strong intention to carry out the plan, while “I might go to the movies tonight” suggests a more tentative or uncertain intention.
“Going To” and Predictions
The “going to” structure is also used to express predictions about the future. In these cases, we’re not necessarily talking about our own intentions but rather our perception of what’s likely to happen. For example, “It’s going to be a hot summer” expresses a prediction based on past experience or current weather patterns. The use of “going to” in this context suggests a degree of certainty, though not an absolute guarantee.
The Temporal Dimension of “Going To”
The way we use “going to” also reveals our perception of time. When we talk about future plans, we’re essentially imagining ourselves in a different point in time. This mental exercise can be a powerful motivator, helping us to stay focused on our goals and visualize the future we desire. The “going to” structure acts as a bridge between our present reality and our desired future, allowing us to connect with the possibilities that lie ahead.
Tips for Mastering “Going To”
1. Be Aware of Your Intention
Before using “going to,” reflect on the level of certainty you want to convey. Are you expressing a firm commitment, a tentative plan, or a prediction? The choice between these levels of intention will influence your choice of words and tone.
2. Use the Right Tense
“Going to” is a future tense construction, so it should be used to express future events. Avoid using it to describe actions that are happening now or have already happened.
3. Pay Attention to Context
The appropriateness of using “going to” depends on the context. In formal settings, you might want to use more formal structures, such as the simple future tense (“I will go”). In informal settings, “going to” is perfectly acceptable.
FAQs About “Going To”
Q: Can “going to” be used to express future actions that are uncertain?
A: Yes, it can. While “going to” often implies a degree of intention or certainty, it can also be used to express events that are not completely definite. For example, “I might be going to the party” implies some uncertainty.
Q: What’s the difference between “going to” and the simple future tense?
A: Both express future events, but “going to” often implies a greater level of intention, planning, or prediction. The simple future tense (“I will go”) can be used for future events that are more tentative or unplanned.
Q: Is “going to” always used with the verb “to be”?
A: Yes, it always requires the verb “to be” in its present tense form (e.g., am, is, are).
Future Tense With Going To Discussing Future Plans
https://youtube.com/watch?v=1dGCQ_L98Cs
Conclusion
The future tense with “going to” is more than just a grammatical structure; it’s a window into our hopes, dreams, and aspirations. It reveals how we perceive and communicate about the future, turning our ambitions into plans and shaping our path forward. So, the next time you use “going to,” take a moment to appreciate the power and versatility of this simple yet effective phrase.
Are you interested in exploring the intricacies of the “going to” future tense and its impact on our communication? Share your thoughts and insights in the comments below.





