Imagine a world where a seemingly ordinary moment – a heavy lifting session, a sudden rush of adrenaline, or even a simple dinner – could trigger a life-altering event. This is the reality for millions of people who live with the constant threat of a heart attack, also known as myocardial infarction (MI). While the prospect of an MI can be daunting, the expertise of nurses plays a critical role in providing a vital lifeline for patients navigating this challenging journey.
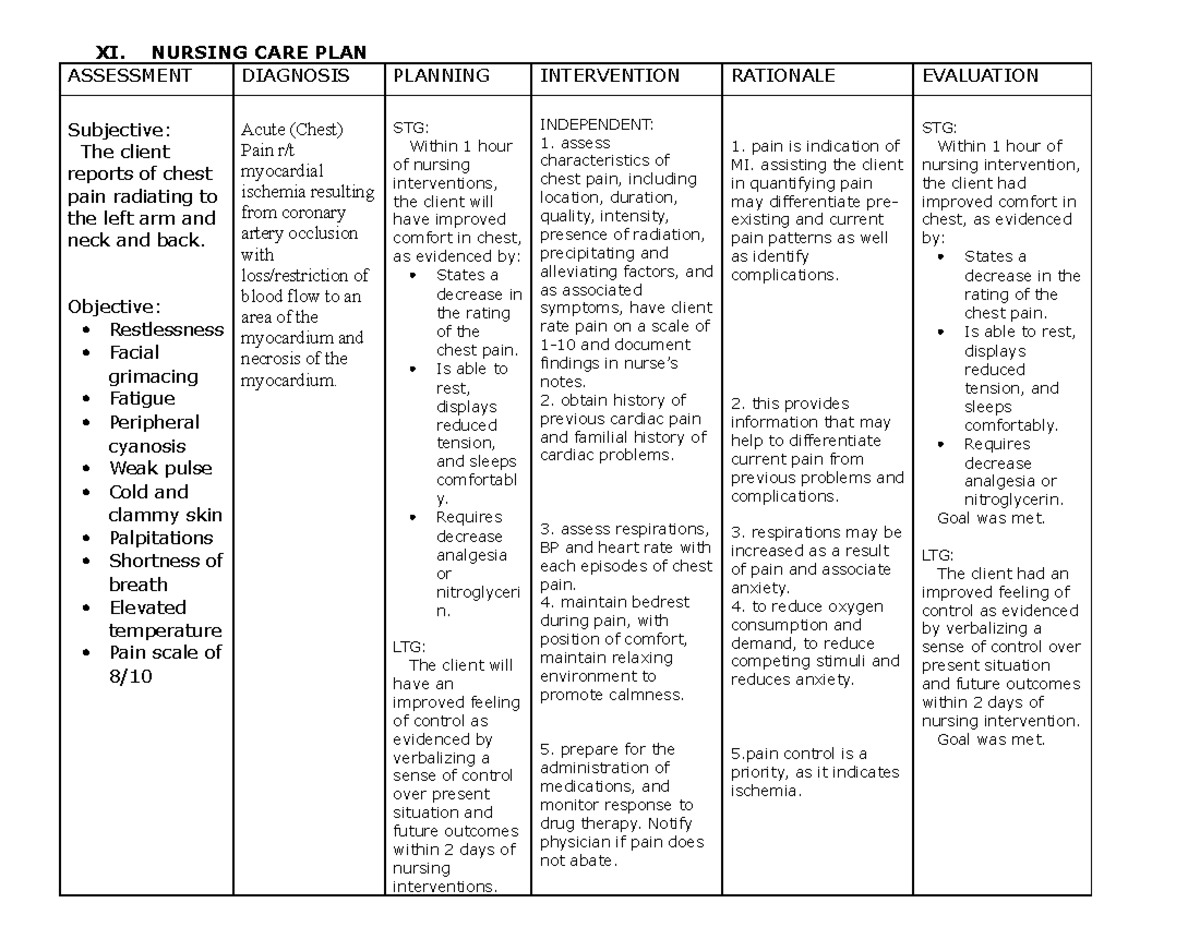
Image: www.studocu.com
A nursing care plan for MI patients is a tailored roadmap for recovery, designed to ensure the best possible outcome. This plan encompasses a comprehensive approach addressing physical, emotional, and psychological needs. It’s much more than just a list of tasks – it’s a commitment to individualized care, based on the unique needs and circumstances of the patient. This article explores the nuances of this crucial plan, outlining its key components and highlighting the essential role nurses play in guiding patients towards a path of healing.
Understanding the Heart of the Matter: Myocardial Infarction
What is a Myocardial Infarction (MI)?
A myocardial infarction, commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when the blood supply to a portion of the heart muscle is abruptly cut off. This interruption, usually caused by a blood clot blocking a coronary artery, deprives the heart tissue of oxygen, leading to damage. The severity of the damage depends on several factors, including the location and duration of the blockage.
The Silent Threat: Recognizing the Signs
While the stereotypical image of a heart attack involves chest pain, the reality can be more nuanced. Many individuals experience atypical symptoms, making recognition challenging. Here are some common warning signs:
- Chest Pain: A squeezing, crushing, or aching sensation in the chest, often radiating to the arms, neck, jaw, or back. This pain may feel like indigestion or heartburn.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing, even with mild exertion or while resting.
- Sweating: Excessive sweating, often accompanied by a feeling of being clammy.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Unusual digestive upset, which may be mistaken for a stomach bug.
- Weakness or Fatigue: Sudden extreme tiredness or weakness.
- Dizziness or lightheadedness: A feeling of faintness or losing consciousness.
- Irregular heartbeat: A skipped beat, fluttering, or racing heart.
It’s crucial to remember that these symptoms can manifest differently in individuals. Recognizing these signs and seeking immediate medical attention can be the difference between life and death.

Image: www.fity.club
The Vital Role of Nurses: Guiding Recovery with Care
Nurses play a critical role in managing and guiding the recovery of MI patients. They work closely with physicians, providing holistic, personalized care that extends beyond medical interventions. The nursing care plan for MI patients is a dynamic document that evolves with the patient’s progress and needs. This plan addresses a multitude of aspects, including:
1. Assessing and Monitoring the Patient
Upon admission, nurses conduct a thorough assessment, gathering information about the patient’s medical history, current symptoms, and vital signs. They monitor the patient’s progress closely, evaluating response to treatment and identifying any potential complications. This continuous monitoring ensures prompt intervention, enhancing the effectiveness of the treatment plan.
2. Promoting Comfort and Pain Management
The aftermath of a heart attack can be extremely painful and discomforting. Nurses provide medication and other comfort measures to alleviate pain and promote rest. They also educate patients about pain management techniques and encourage them to communicate their needs effectively.
3. Supporting Physical Activity and Rehabilitation
As the patient recovers, nurses encourage controlled physical activity, tailored to their individual abilities. This gradual increase in activity helps strengthen the heart muscle and improve overall fitness. They provide guidance on exercises and lifestyle changes, emphasizing the importance of regular movement for long-term heart health.
4. Educating and Empowering the Patient
Nurses play a crucial role in educating MI patients about their condition, treatment plan, and the importance of lifestyle modifications. They explain medication regimens, discuss risk factors, and encourage healthy habits such as diet changes and stress management. Empowering patients to actively participate in their recovery process is a key aspect of their care.
Key Components of the Nursing Care Plan for MI Patients
The nursing care plan is a detailed roadmap tailored to the individual needs of each MI patient. Here are some key components that are commonly included:
1. Cardiovascular Monitoring:
This includes continuous electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring to assess heart rhythm and detect any abnormalities. Nurses regularly check blood pressure, pulse rate, and oxygen saturation to ensure the patient is stable and responding to treatment.
2. Medication Administration:
Nurses carefully administer prescribed medications, such as:
- Antiplatelet agents: These medications reduce the risk of blood clot formation, preventing further blockage of the coronary arteries.
- Nitrates: These medications work by dilating blood vessels, improving blood flow and reducing the workload of the heart.
- Beta-blockers: These medications work by slowing down the heart rate and reducing blood pressure, lessening the strain on the heart.
- ACE inhibitors: These medications help relax blood vessels and improve blood flow, protecting the heart from further damage.
- Statins: These medications lower cholesterol levels, which can help prevent future heart attacks.
Nurses also educate patients about their medications, explaining dosage, side effects, and potential drug interactions.
3. Oxygen Therapy:
Supplying supplemental oxygen can be critical in the initial stages of recovery, improving blood oxygen levels and ensuring adequate oxygenation of the heart muscle. Nurses carefully monitor oxygen levels and adjust the flow rate as needed.
4. Fluid Management:
Nurses carefully monitor fluid intake and output, ensuring adequate hydration and preventing fluid build-up that could strain the heart. This also helps assess kidney function, which is crucial in the recovery process.
5. Nutritional Counseling:
Nurses work with registered dieticians to create a personalized diet plan that promotes heart health. This typically involves reducing saturated and trans fats, limiting sodium, and increasing fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. They provide education and guidance on heart-healthy eating habits to help patients maintain a long-term healthy lifestyle.
6. Emotional Support:
The experience of a heart attack can be emotionally challenging. Nurses provide a calming presence, offering reassurance and answering questions. They understand the importance of psychosocial support in this stressful period, encouraging patients to express their fears and concerns openly. This empathetic approach fosters a sense of trust and support, empowering patients to cope with their emotions effectively.
7. Discharge Planning:
As recovery progresses, nurses play a crucial role in discharge planning. They collaborate with other healthcare professionals to ensure a smooth transition back home. They provide detailed instructions about medications, dietary restrictions, follow-up appointments, and lifestyle modifications. This thorough approach ensures that patients have the knowledge and support they need to manage their health effectively beyond the hospital setting.
Navigating the Future: Long-Term Management
The acute phase of recovery is just the beginning of a long-term journey for MI patients. Nurses continue to guide and support them, emphasizing the importance of continued self-care and adherence to the treatment plan. This long-term management includes:
1. Lifestyle Modifications:
Nurses encourage patients to embrace lasting lifestyle changes that reduce the risk of future heart problems. This includes:
- Healthy Diet: Maintaining a heart-healthy diet low in saturated fat, cholesterol, and sodium is crucial.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity helps strengthen the heart muscle, improve blood flow, and reduce stress.
- Quitting Smoking: Smoking heavily increases the risk of heart disease, making it a critical factor to address. Nurses provide support and resources to help patients quit smoking successfully.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can put a strain on the heart. Nurses recommend stress reduction techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
2. Follow-Up Care:
Nurses ensure that patients follow up with their physician regularly for checkups, medication refills, and overall health monitoring. They connect patients with cardiac rehabilitation programs, which are designed to help individuals recover from a heart attack and improve their overall fitness.
Nursing Care Plan For Mi Patient
Conclusion
The nursing care plan for MI patients is a vital lifeline, providing comprehensive support and guidance throughout the recovery journey. Nurses are essential partners in this process, offering compassionate care, expert knowledge, and unwavering support. They go beyond medical interventions, addressing physical, emotional, and psychological needs, empowering patients to navigate their recovery with strength and resilience. This personalized approach ensures that MI patients receive the best possible care, ultimately giving them a fighting chance at a healthy and fulfilling future.





