Have you ever looked at a circuit diagram and felt like you were staring at an alien language? Those squiggly lines and cryptic symbols might seem intimidating, but they hold the key to understanding the fascinating world of electronics. Every component, from a humble resistor to a powerful microprocessor, has its own unique symbol, a visual shorthand that allows engineers and technicians to communicate complex ideas with ease. This guide will take you on a journey into the heart of electronics, unveiling the meaning behind these often overlooked symbols and equipping you with the knowledge to decipher any circuit diagram.
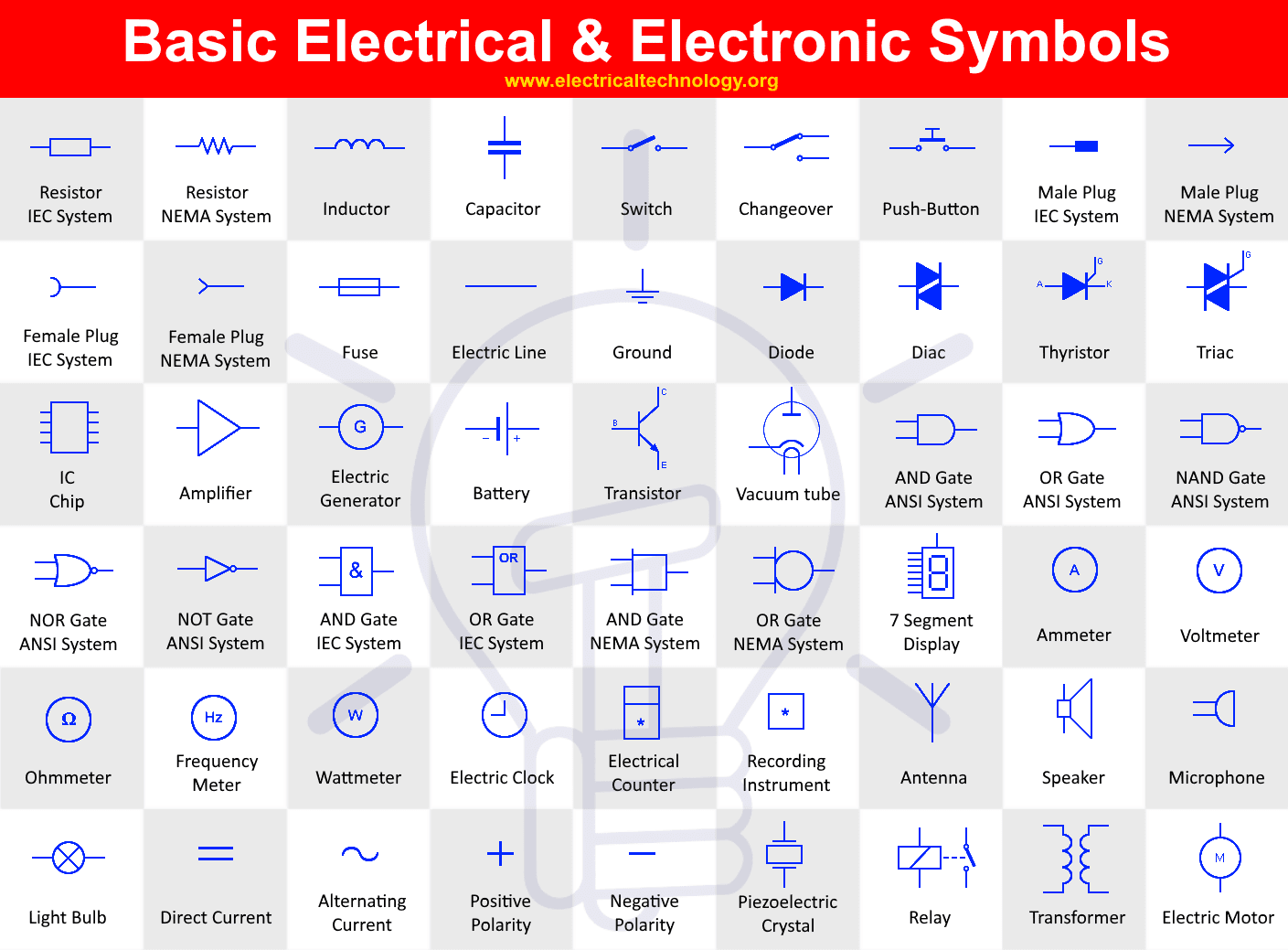
Image: www.electricaltechnology.org
Imagine being able to build your own robots, repair your gadgets, or even design your own electronic circuits. Understanding electronic component symbols is the first step on that exciting path. Whether you’re a curious tinkerer, a budding electronics enthusiast, or a seasoned professional, this guide provides a clear and accessible roadmap to mastering the language of electronics. We’ll delve into the history of electronic symbols, explore the common components you’ll encounter, and provide practical tips for learning and remembering them. Get ready to unlock the secrets of electronics and discover a world of possibilities at your fingertips.
The Language of Electronics: A Glimpse into History
The history of electronic symbols is intertwined with the evolution of electronics itself. Early pioneers of electrical engineering, like Thomas Edison and Nikola Tesla, experimented with different ways to represent electrical components in their schematics. As technology advanced, the need for a standardized system became apparent. In the early 20th century, the American Institute of Electrical Engineers (AIEE) and the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) played a key role in developing a set of universally recognized symbols. These symbols, often referred to as “schematic symbols,” have become the standard language for electrical and electronic diagrams throughout the world.
Essential Electronic Components and Their Symbols
Let’s dive into the world of electronic symbols by exploring some of the most fundamental components:
1. Resistors: The Flow Controllers
Resistors are the gatekeepers of current flow. They limit the amount of electric current passing through them, acting like a narrow pipe for electrons. The symbol for a resistor is a simple rectangle, often with zig-zag lines inside to represent its resistance.
Symbol: 

Image: www.microscopio.pro
2. Capacitors: The Energy Storers
Capacitors are like miniature energy banks, storing electrical charge. They can release that charge quickly, acting like tiny bursts of power. The symbol for a capacitor is typically two parallel lines, representing the capacitor’s plates.
Symbol: 
3. Inductors: The Current Opposers
Inductors resist changes in electrical current. They’re like stubborn magnets that oppose any attempt to increase or decrease the current flow. The symbol for an inductor is a coil, representing the wire wound around a core.
Symbol: 
4. Diodes: The One-Way Streets
Diodes are like one-way streets for current. They allow electricity to flow in only one direction. The symbol for a diode is an arrow pointing to a vertical line.
Symbol: 
5. Transistors: The Amplifiers and Switches
Transistors are the workhorses of modern electronics. They can amplify signals, control the flow of current, and act as switches. There are two main types of transistors: Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs) and Field-Effect Transistors (FETs). Each has a distinct symbol.
Symbol (BJT): 
Symbol (FET): 
6. Integrated Circuits (ICs): The Tiny Brains
ICs, also known as microchips, encapsulate complex circuits on a single tiny chip. They can perform logic operations, process data, and control other components. The symbol for an IC is a rectangle with pins on the sides, representing the connections.
Symbol: 
7. Soldering Points and Junctions
These symbols are crucial for understanding how components are physically connected in a circuit.
Symbol: 
8. Wires and Connections
Wires are the pathways for electricity to flow between components.
Symbol: A solid line represents a wire connection.
9. Ground (GND)
This symbol represents the reference point for voltage.
Symbol: A triangle with a solid line inside.
Beyond the Basics: Additional Components
The world of electronic components is vast. Beyond the core components like resistors, capacitors, and transistors, there are numerous other specialized components with their own unique symbols. These include:
- Op-amps: These versatile components are used for amplifying, filtering, and manipulating signals.
- LEDs: Light-emitting diodes produce light when current flows through them.
- Sensors: These devices convert physical quantities like light, temperature, or pressure into electrical signals.
- Relays: These electromechanical switches control the flow of current using electromagnetic coils.
- Microcontrollers: These powerful ICs can execute instructions, communicate with other devices, and manage multiple tasks.
While each of these components has its own unique symbol, the fundamental principles of circuit diagrams remain consistent. Learning to decipher the basic symbols will provide you with the foundation to understand more complex circuits.
Finding and Using PDFs of Electronic Component Symbols and Pictures
Many resources are available to help you expand your knowledge of electronic symbols. Here are a few ways to find comprehensive PDFs that contain a vast collection of symbols and pictures:
- Online Databases: Websites like Wikimedia Commons and Digi-Key offer extensive libraries of electronic symbols. Many of these resources can be downloaded as PDFs for easy reference.
- Educational Institutions: Colleges and universities often make their course materials available online, including PDFs of circuit diagrams with detailed symbol explanations.
- Technical Manuals: Manufacturers often provide comprehensive technical manuals that include schematic diagrams and symbol explanations for their specific components.
Mastering the Language of Electronics: Tips for Success
Learning to interpret electronic symbols is not just about memorizing a set of pictures. It’s about understanding the function of each component and how they interact within a circuit. Here are a few tips to enhance your learning:
- Start with the basics: Focus on mastering the symbols for the most commonly used components.
- Use visual aids: Create flashcards or posters with the symbols and their corresponding component names.
- Practice, practice, practice: The more you practice interpreting circuit diagrams, the quicker you’ll become at recognizing the symbols.
- Experiment with real circuits: Building your own simple circuits is a great way to solidify your understanding of how components work together.
The Power of Understanding Electronic Components
The ability to read electronic circuit diagrams opens a door to a world of possibilities. With increased confidence in interpreting these diagrams, you’re equipped to:
- Build your own electronics projects: From simple circuits to complex gadgets, the ability to understand symbols empowers you to bring your ideas to life.
- Repair your own devices: Knowing the symbols allows you to troubleshoot problems and fix broken gadgets.
- Contribute to the world of innovation: Comprehending the language of electronics is a crucial skill for anyone who wants to make a lasting impact in the field of technology.
Electronic Components Symbols And Pictures Pdf
Conclusion
The world of electronics is vast and constantly evolving, but mastering the fundamentals is essential for anyone who wants to engage with this exciting field. Electronic component symbols are a visual language that unlocks the mysteries of circuits, allowing you to communicate complex ideas with ease. Don’t be intimidated by the seemingly cryptic symbols; they are the key to unlocking innovation and bringing your electronic dreams to reality. With resources available online and a commitment to practice, you can embark on your journey to becoming an electronics maestro. Let your curiosity guide you, and remember, electronics is a language waiting to be deciphered.





